搜索到
152
篇与
的结果
-
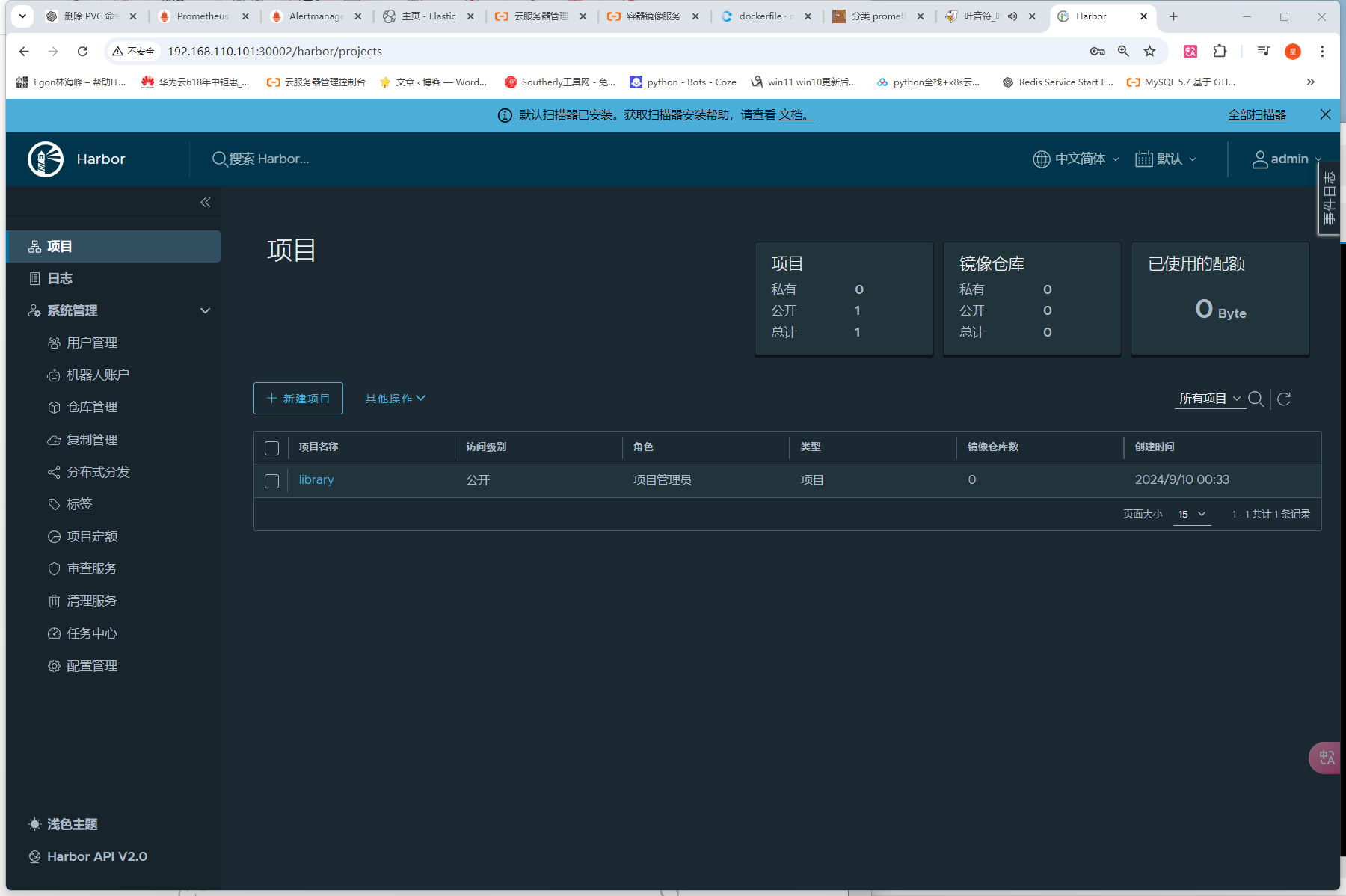
 安装harbor Harbor 是一个主流的镜像仓库系统,在 v1.6 版本以后的 harbor 中新增加了 helm charts 的管理功能,可以存储Chart文件。 其实在Harbor 2.8+版本中,Helm Chart支持已经转移到了OCI(Open Container Initiative)格式。这意味着你需要使用OCI形式来上传和管理你的Helm Chart(不需要像网上一样,去为harbor开启chart仓库支持)一、安装一个nfs存储,提供一个sc默认存储类# 1、安装 helm repo add nfs-subdir-external-provisioner https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/ helm upgrade --install nfs-subdir-external-provisioner nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner --set nfs.server=192.168.110.101 --set nfs.path=/data/nfs --set storageClass.defaultClass=true -n kube-system # 2、查看 helm -n kube-system list # 3、查看nfs_provider的pod kubectl -n kube-system get pods |grep nfs nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-797c875548-rt4dh 1/1 Running 2 (58m ago) 23h # 4、查看sc(已经设置为默认的了) kubectl -n kube-system get sc nfs-client NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE nfs-client (default) cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner Delete Immediate true 23h 二、添加仓库地址helm repo add harbor https://helm.goharbor.io helm repo list三、下载Chart包到本地因为需要修改的参数比较多,在命令行直接helm install比较复杂,我就将Chart包下载到本地,再修改一些配置,这样比较直观,也比较符合实际工作中的业务环境。helm pull harbor/harbor # 下载Chart包 tar zxvf harbor-1.14.2.tgz # 解压包四、修改values.yamlexpose: # Set how to expose the service. Set the type as "ingress", "clusterIP", "nodePort" or "loadBalancer" # and fill the information in the corresponding section type: nodePort tls: # Enable TLS or not. # Delete the "ssl-redirect" annotations in "expose.ingress.annotations" when TLS is disabled and "expose.type" is "ingress" # Note: if the "expose.type" is "ingress" and TLS is disabled, # the port must be included in the command when pulling/pushing images. # Refer to https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/5291 for details. enabled: false # The source of the tls certificate. Set as "auto", "secret" # or "none" and fill the information in the corresponding section # 1) auto: generate the tls certificate automatically # 2) secret: read the tls certificate from the specified secret. # The tls certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager # 3) none: configure no tls certificate for the ingress. If the default # tls certificate is configured in the ingress controller, choose this option certSource: auto auto: # The common name used to generate the certificate, it's necessary # when the type isn't "ingress" commonName: "" secret: # The name of secret which contains keys named: # "tls.crt" - the certificate # "tls.key" - the private key secretName: "" ingress: hosts: core: core.harbor.domain # set to the type of ingress controller if it has specific requirements. # leave as `default` for most ingress controllers. # set to `gce` if using the GCE ingress controller # set to `ncp` if using the NCP (NSX-T Container Plugin) ingress controller # set to `alb` if using the ALB ingress controller # set to `f5-bigip` if using the F5 BIG-IP ingress controller controller: default ## Allow .Capabilities.KubeVersion.Version to be overridden while creating ingress kubeVersionOverride: "" className: "" annotations: # note different ingress controllers may require a different ssl-redirect annotation # for Envoy, use ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "true" and remove the nginx lines below ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true" ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "0" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "0" # ingress-specific labels labels: {} clusterIP: # The name of ClusterIP service name: harbor # The ip address of the ClusterIP service (leave empty for acquiring dynamic ip) staticClusterIP: "" ports: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP httpPort: 80 # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS httpsPort: 443 # Annotations on the ClusterIP service annotations: {} # ClusterIP-specific labels labels: {} nodePort: # The name of NodePort service name: harbor ports: http: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP port: 80 # The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP nodePort: 30002 https: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS port: 443 # The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS nodePort: 30003 # Annotations on the nodePort service annotations: {} # nodePort-specific labels labels: {} loadBalancer: # The name of LoadBalancer service name: harbor # Set the IP if the LoadBalancer supports assigning IP IP: "" ports: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP httpPort: 80 # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS httpsPort: 443 # Annotations on the loadBalancer service annotations: {} # loadBalancer-specific labels labels: {} sourceRanges: [] # The external URL for Harbor core service. It is used to # 1) populate the docker/helm commands showed on portal # 2) populate the token service URL returned to docker client # # Format: protocol://domain[:port]. Usually: # 1) if "expose.type" is "ingress", the "domain" should be # the value of "expose.ingress.hosts.core" # 2) if "expose.type" is "clusterIP", the "domain" should be # the value of "expose.clusterIP.name" # 3) if "expose.type" is "nodePort", the "domain" should be # the IP address of k8s node # # If Harbor is deployed behind the proxy, set it as the URL of proxy externalURL: http://192.168.110.101:30002 # The persistence is enabled by default and a default StorageClass # is needed in the k8s cluster to provision volumes dynamically. # Specify another StorageClass in the "storageClass" or set "existingClaim" # if you already have existing persistent volumes to use # # For storing images and charts, you can also use "azure", "gcs", "s3", # "swift" or "oss". Set it in the "imageChartStorage" section persistence: enabled: true # Setting it to "keep" to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete # operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart deleted # (this does not apply for PVCs that are created for internal database # and redis components, i.e. they are never deleted automatically) resourcePolicy: "keep" persistentVolumeClaim: registry: # Use the existing PVC which must be created manually before bound, # and specify the "subPath" if the PVC is shared with other components existingClaim: "" # Specify the "storageClass" used to provision the volume. Or the default # StorageClass will be used (the default). # Set it to "-" to disable dynamic provisioning storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 5Gi annotations: {} jobservice: jobLog: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi annotations: {} # If external database is used, the following settings for database will # be ignored database: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi annotations: {} # If external Redis is used, the following settings for Redis will # be ignored redis: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi annotations: {} trivy: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 5Gi annotations: {} # Define which storage backend is used for registry to store # images and charts. Refer to # https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/main/docs/content/about/configuration.md#storage # for the detail. imageChartStorage: # Specify whether to disable `redirect` for images and chart storage, for # backends which not supported it (such as using minio for `s3` storage type), please disable # it. To disable redirects, simply set `disableredirect` to `true` instead. # Refer to # https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/main/docs/configuration.md#redirect # for the detail. disableredirect: false # Specify the "caBundleSecretName" if the storage service uses a self-signed certificate. # The secret must contain keys named "ca.crt" which will be injected into the trust store # of registry's containers. # caBundleSecretName: # Specify the type of storage: "filesystem", "azure", "gcs", "s3", "swift", # "oss" and fill the information needed in the corresponding section. The type # must be "filesystem" if you want to use persistent volumes for registry type: filesystem filesystem: rootdirectory: /storage #maxthreads: 100 azure: accountname: accountname accountkey: base64encodedaccountkey container: containername #realm: core.windows.net # To use existing secret, the key must be AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY existingSecret: "" gcs: bucket: bucketname # The base64 encoded json file which contains the key encodedkey: base64-encoded-json-key-file #rootdirectory: /gcs/object/name/prefix #chunksize: "5242880" # To use existing secret, the key must be GCS_KEY_DATA existingSecret: "" useWorkloadIdentity: false s3: # Set an existing secret for S3 accesskey and secretkey # keys in the secret should be REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_ACCESSKEY and REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_SECRETKEY for registry #existingSecret: "" region: us-west-1 bucket: bucketname #accesskey: awsaccesskey #secretkey: awssecretkey #regionendpoint: http://myobjects.local #encrypt: false #keyid: mykeyid #secure: true #skipverify: false #v4auth: true #chunksize: "5242880" #rootdirectory: /s3/object/name/prefix #storageclass: STANDARD #multipartcopychunksize: "33554432" #multipartcopymaxconcurrency: 100 #multipartcopythresholdsize: "33554432" swift: authurl: https://storage.myprovider.com/v3/auth username: username password: password container: containername # keys in existing secret must be REGISTRY_STORAGE_SWIFT_PASSWORD, REGISTRY_STORAGE_SWIFT_SECRETKEY, REGISTRY_STORAGE_SWIFT_ACCESSKEY existingSecret: "" #region: fr #tenant: tenantname #tenantid: tenantid #domain: domainname #domainid: domainid #trustid: trustid #insecureskipverify: false #chunksize: 5M #prefix: #secretkey: secretkey #accesskey: accesskey #authversion: 3 #endpointtype: public #tempurlcontainerkey: false #tempurlmethods: oss: accesskeyid: accesskeyid accesskeysecret: accesskeysecret region: regionname bucket: bucketname # key in existingSecret must be REGISTRY_STORAGE_OSS_ACCESSKEYSECRET existingSecret: "" #endpoint: endpoint #internal: false #encrypt: false #secure: true #chunksize: 10M #rootdirectory: rootdirectory # The initial password of Harbor admin. Change it from portal after launching Harbor # or give an existing secret for it # key in secret is given via (default to HARBOR_ADMIN_PASSWORD) # existingSecretAdminPassword: existingSecretAdminPasswordKey: HARBOR_ADMIN_PASSWORD harborAdminPassword: "Harbor12345" # The internal TLS used for harbor components secure communicating. In order to enable https # in each component tls cert files need to provided in advance. internalTLS: # If internal TLS enabled enabled: false # enable strong ssl ciphers (default: false) strong_ssl_ciphers: false # There are three ways to provide tls # 1) "auto" will generate cert automatically # 2) "manual" need provide cert file manually in following value # 3) "secret" internal certificates from secret certSource: "auto" # The content of trust ca, only available when `certSource` is "manual" trustCa: "" # core related cert configuration core: # secret name for core's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of core's TLS cert file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of core's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # jobservice related cert configuration jobservice: # secret name for jobservice's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of jobservice's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of jobservice's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # registry related cert configuration registry: # secret name for registry's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of registry's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of registry's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # portal related cert configuration portal: # secret name for portal's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of portal's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of portal's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # trivy related cert configuration trivy: # secret name for trivy's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of trivy's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of trivy's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" ipFamily: # ipv6Enabled set to true if ipv6 is enabled in cluster, currently it affected the nginx related component ipv6: enabled: true # ipv4Enabled set to true if ipv4 is enabled in cluster, currently it affected the nginx related component ipv4: enabled: true imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent # Use this set to assign a list of default pullSecrets imagePullSecrets: # - name: docker-registry-secret # - name: internal-registry-secret # The update strategy for deployments with persistent volumes(jobservice, registry): "RollingUpdate" or "Recreate" # Set it as "Recreate" when "RWM" for volumes isn't supported updateStrategy: type: RollingUpdate # debug, info, warning, error or fatal logLevel: info # The name of the secret which contains key named "ca.crt". Setting this enables the # download link on portal to download the CA certificate when the certificate isn't # generated automatically caSecretName: "" # The secret key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars. secretKey: "not-a-secure-key" # If using existingSecretSecretKey, the key must be secretKey existingSecretSecretKey: "" # The proxy settings for updating trivy vulnerabilities from the Internet and replicating # artifacts from/to the registries that cannot be reached directly proxy: httpProxy: httpsProxy: noProxy: 127.0.0.1,localhost,.local,.internal components: - core - jobservice - trivy # Run the migration job via helm hook enableMigrateHelmHook: false # The custom ca bundle secret, the secret must contain key named "ca.crt" # which will be injected into the trust store for core, jobservice, registry, trivy components # caBundleSecretName: "" ## UAA Authentication Options # If you're using UAA for authentication behind a self-signed # certificate you will need to provide the CA Cert. # Set uaaSecretName below to provide a pre-created secret that # contains a base64 encoded CA Certificate named `ca.crt`. # uaaSecretName: metrics: enabled: true core: path: /metrics port: 8001 registry: path: /metrics port: 8001 jobservice: path: /metrics port: 8001 exporter: path: /metrics port: 8001 ## Create prometheus serviceMonitor to scrape harbor metrics. ## This requires the monitoring.coreos.com/v1 CRD. Please see ## https://github.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/blob/main/Documentation/user-guides/getting-started.md ## serviceMonitor: enabled: false additionalLabels: {} # Scrape interval. If not set, the Prometheus default scrape interval is used. interval: "" # Metric relabel configs to apply to samples before ingestion. metricRelabelings: [] # - action: keep # regex: 'kube_(daemonset|deployment|pod|namespace|node|statefulset).+' # sourceLabels: [__name__] # Relabel configs to apply to samples before ingestion. relabelings: [] # - sourceLabels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] # separator: ; # regex: ^(.*)$ # targetLabel: nodename # replacement: $1 # action: replace trace: enabled: false # trace provider: jaeger or otel # jaeger should be 1.26+ provider: jaeger # set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth sample_rate: 1 # namespace used to differentiate different harbor services # namespace: # attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider # attributes: # application: harbor jaeger: # jaeger supports two modes: # collector mode(uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed) # agent mode(uncomment agent_host and agent_port) endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces # username: # password: # agent_host: hostname # export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode # agent_port: 6831 otel: endpoint: hostname:4318 url_path: /v1/traces compression: false insecure: true # timeout is in seconds timeout: 10 # cache layer configurations # if this feature enabled, harbor will cache the resource # `project/project_metadata/repository/artifact/manifest` in the redis # which help to improve the performance of high concurrent pulling manifest. cache: # default is not enabled. enabled: false # default keep cache for one day. expireHours: 24 ## set Container Security Context to comply with PSP restricted policy if necessary ## each of the conatiner will apply the same security context ## containerSecurityContext:{} is initially an empty yaml that you could edit it on demand, we just filled with a common template for convenience containerSecurityContext: privileged: false allowPrivilegeEscalation: false seccompProfile: type: RuntimeDefault runAsNonRoot: true capabilities: drop: - ALL # If service exposed via "ingress", the Nginx will not be used nginx: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/nginx-photon tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: portal: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/harbor-portal tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## Additional service annotations serviceAnnotations: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] core: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/harbor-core tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 ## Startup probe values startupProbe: enabled: true initialDelaySeconds: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## Additional service annotations serviceAnnotations: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] ## User settings configuration json string configureUserSettings: # The provider for updating project quota(usage), there are 2 options, redis or db. # By default it is implemented by db but you can configure it to redis which # can improve the performance of high concurrent pushing to the same project, # and reduce the database connections spike and occupies. # Using redis will bring up some delay for quota usage updation for display, so only # suggest switch provider to redis if you were ran into the db connections spike around # the scenario of high concurrent pushing to same project, no improvment for other scenes. quotaUpdateProvider: db # Or redis # Secret is used when core server communicates with other components. # If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one. Alternatively set existingSecret to use an existing secret # Must be a string of 16 chars. secret: "" # Fill in the name of a kubernetes secret if you want to use your own # If using existingSecret, the key must be secret existingSecret: "" # Fill the name of a kubernetes secret if you want to use your own # TLS certificate and private key for token encryption/decryption. # The secret must contain keys named: # "tls.key" - the private key # "tls.crt" - the certificate secretName: "" # If not specifying a preexisting secret, a secret can be created from tokenKey and tokenCert and used instead. # If none of secretName, tokenKey, and tokenCert are specified, an ephemeral key and certificate will be autogenerated. # tokenKey and tokenCert must BOTH be set or BOTH unset. # The tokenKey value is formatted as a multiline string containing a PEM-encoded RSA key, indented one more than tokenKey on the following line. tokenKey: | # If tokenKey is set, the value of tokenCert must be set as a PEM-encoded certificate signed by tokenKey, and supplied as a multiline string, indented one more than tokenCert on the following line. tokenCert: | # The XSRF key. Will be generated automatically if it isn't specified xsrfKey: "" # If using existingSecret, the key is defined by core.existingXsrfSecretKey existingXsrfSecret: "" # If using existingSecret, the key existingXsrfSecretKey: CSRF_KEY # The time duration for async update artifact pull_time and repository # pull_count, the unit is second. Will be 10 seconds if it isn't set. # eg. artifactPullAsyncFlushDuration: 10 artifactPullAsyncFlushDuration: gdpr: deleteUser: false auditLogsCompliant: false jobservice: image: repository: goharbor/harbor-jobservice tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] maxJobWorkers: 10 # The logger for jobs: "file", "database" or "stdout" jobLoggers: - file # - database # - stdout # The jobLogger sweeper duration (ignored if `jobLogger` is `stdout`) loggerSweeperDuration: 14 #days notification: webhook_job_max_retry: 3 webhook_job_http_client_timeout: 3 # in seconds reaper: # the max time to wait for a task to finish, if unfinished after max_update_hours, the task will be mark as error, but the task will continue to run, default value is 24 max_update_hours: 24 # the max time for execution in running state without new task created max_dangling_hours: 168 # Secret is used when job service communicates with other components. # If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one. # Must be a string of 16 chars. secret: "" # Use an existing secret resource existingSecret: "" # Key within the existing secret for the job service secret existingSecretKey: JOBSERVICE_SECRET registry: registry: image: repository: goharbor/registry-photon tag: v2.11.1 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] controller: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/harbor-registryctl tag: v2.11.1 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # Secret is used to secure the upload state from client # and registry storage backend. # See: https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/main/docs/configuration.md#http # If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one. # Must be a string of 16 chars. secret: "" # Use an existing secret resource existingSecret: "" # Key within the existing secret for the registry service secret existingSecretKey: REGISTRY_HTTP_SECRET # If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL. relativeurls: false credentials: username: "harbor_registry_user" password: "harbor_registry_password" # If using existingSecret, the key must be REGISTRY_PASSWD and REGISTRY_HTPASSWD existingSecret: "" # Login and password in htpasswd string format. Excludes `registry.credentials.username` and `registry.credentials.password`. May come in handy when integrating with tools like argocd or flux. This allows the same line to be generated each time the template is rendered, instead of the `htpasswd` function from helm, which generates different lines each time because of the salt. # htpasswdString: $apr1$XLefHzeG$Xl4.s00sMSCCcMyJljSZb0 # example string htpasswdString: "" middleware: enabled: false type: cloudFront cloudFront: baseurl: example.cloudfront.net keypairid: KEYPAIRID duration: 3000s ipfilteredby: none # The secret key that should be present is CLOUDFRONT_KEY_DATA, which should be the encoded private key # that allows access to CloudFront privateKeySecret: "my-secret" # enable purge _upload directories upload_purging: enabled: true # remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week. age: 168h # the interval of the purge operations interval: 24h dryrun: false trivy: # enabled the flag to enable Trivy scanner enabled: true image: # repository the repository for Trivy adapter image repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/adapter-photon # tag the tag for Trivy adapter image tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false # replicas the number of Pod replicas replicas: 1 resources: requests: cpu: 200m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 1 memory: 1Gi extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # debugMode the flag to enable Trivy debug mode with more verbose scanning log debugMode: false # vulnType a comma-separated list of vulnerability types. Possible values are `os` and `library`. vulnType: "os,library" # severity a comma-separated list of severities to be checked severity: "UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL" # ignoreUnfixed the flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities ignoreUnfixed: false # insecure the flag to skip verifying registry certificate insecure: false # gitHubToken the GitHub access token to download Trivy DB # # Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases. # It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached # in the local file system (`/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db/trivy.db`). In addition, the database contains the update # timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. # Currently, the database is updated every 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub. # # Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough # for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000 # requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult # https://developer.github.com/v3/#rate-limiting # # You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in # https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line gitHubToken: "" # skipUpdate the flag to disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub # # You might want to set the value of this flag to `true` in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues. # If the value is set to `true` you have to manually download the `trivy.db` file and mount it in the # `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db/trivy.db` path. skipUpdate: false # skipJavaDBUpdate If the flag is enabled you have to manually download the `trivy-java.db` file and mount it in the # `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/java-db/trivy-java.db` path # skipJavaDBUpdate: false # The offlineScan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. # # Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it. # For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't # exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode. # It would work if all the dependencies are in local. # This option doesn’t affect DB download. You need to specify skipUpdate as well as offlineScan in an air-gapped environment. offlineScan: false # Comma-separated list of what security issues to detect. Possible values are `vuln`, `config` and `secret`. Defaults to `vuln`. securityCheck: "vuln" # The duration to wait for scan completion timeout: 5m0s database: # if external database is used, set "type" to "external" # and fill the connection information in "external" section type: internal internal: image: repository: goharbor/harbor-db tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m # The timeout used in livenessProbe; 1 to 5 seconds livenessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 1 # The timeout used in readinessProbe; 1 to 5 seconds readinessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 1 extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. extrInitContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # The initial superuser password for internal database password: "changeit" # The size limit for Shared memory, pgSQL use it for shared_buffer # More details see: # https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/15034 shmSizeLimit: 512Mi initContainer: migrator: {} # resources: # requests: # memory: 128Mi # cpu: 100m permissions: {} # resources: # requests: # memory: 128Mi # cpu: 100m external: host: "192.168.0.1" port: "5432" username: "user" password: "password" coreDatabase: "registry" # if using existing secret, the key must be "password" existingSecret: "" # "disable" - No SSL # "require" - Always SSL (skip verification) # "verify-ca" - Always SSL (verify that the certificate presented by the # server was signed by a trusted CA) # "verify-full" - Always SSL (verify that the certification presented by the # server was signed by a trusted CA and the server host name matches the one # in the certificate) sslmode: "disable" # The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool per pod (core+exporter). # If it <=0, no idle connections are retained. maxIdleConns: 100 # The maximum number of open connections to the database per pod (core+exporter). # If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections. # Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for harbor's postgres. maxOpenConns: 900 ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} redis: # if external Redis is used, set "type" to "external" # and fill the connection information in "external" section type: internal internal: image: repository: goharbor/redis-photon tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # # jobserviceDatabaseIndex defaults to "1" # # registryDatabaseIndex defaults to "2" # # trivyAdapterIndex defaults to "5" # # harborDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "6", this config is optional # # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "7", this config is optional jobserviceDatabaseIndex: "1" registryDatabaseIndex: "2" trivyAdapterIndex: "5" # harborDatabaseIndex: "6" # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex: "7" external: # support redis, redis+sentinel # addr for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis> # addr for redis+sentinel: <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3> addr: "192.168.0.2:6379" # The name of the set of Redis instances to monitor, it must be set to support redis+sentinel sentinelMasterSet: "" # The "coreDatabaseIndex" must be "0" as the library Harbor # used doesn't support configuring it # harborDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "6", this config is optional # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "7", this config is optional coreDatabaseIndex: "0" jobserviceDatabaseIndex: "1" registryDatabaseIndex: "2" trivyAdapterIndex: "5" # harborDatabaseIndex: "6" # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex: "7" # username field can be an empty string, and it will be authenticated against the default user username: "" password: "" # If using existingSecret, the key must be REDIS_PASSWORD existingSecret: "" ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} exporter: image: repository: goharbor/harbor-exporter tag: v2.11.1 serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule cacheDuration: 23 cacheCleanInterval: 14400 五、安装kubectl create namespace harbor helm install harbor . -n harbor # 将安装资源部署到harbor命名空间 # 注意 # 1、部署过程可能因为下载镜像慢导致redis尚未启动成功,其他pod会出现启动失败的现象,耐心等一会即可 # 2、如果下载速度过慢,可以自己制作镜像,或者下载镜像后上传到服务器导入 # nerdctl -n k8s.io load -i xxxxxxxxxxx.tar六、查看[root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 0/1 Running 2 (66s ago) 3m21s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (79s ago) 3m21s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 5 (6s ago) 3m21s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 3m21s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 0/1 Running 2 (77s ago) 3m32s harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (78s ago) 3m33s ^C[root@master01 harbor]# ^C [root@master01 harbor]# ^C [root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor delete pod harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26 & [1] 103883 [root@master01 harbor]# pod "harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26" deleted [1]+ 完成 kubectl -n harbor delete pod harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26 [root@master01 harbor]# [root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (2m13s ago) 4m28s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (2m26s ago) 4m28s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 0/1 Running 0 6s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 4m28s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m28s ^C[root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (2m26s ago) 4m41s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (2m39s ago) 4m41s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 0/1 Running 0 19s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 4m41s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 1/1 Running 0 21s ^C[root@master01 harbor]# ^C [root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (2m31s ago) 4m46s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (2m44s ago) 4m46s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 1/1 Running 0 24s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 4m46s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m46s七、登录http://192.168.110.101:30002,账号:admin 密码:Harbor12345
安装harbor Harbor 是一个主流的镜像仓库系统,在 v1.6 版本以后的 harbor 中新增加了 helm charts 的管理功能,可以存储Chart文件。 其实在Harbor 2.8+版本中,Helm Chart支持已经转移到了OCI(Open Container Initiative)格式。这意味着你需要使用OCI形式来上传和管理你的Helm Chart(不需要像网上一样,去为harbor开启chart仓库支持)一、安装一个nfs存储,提供一个sc默认存储类# 1、安装 helm repo add nfs-subdir-external-provisioner https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/ helm upgrade --install nfs-subdir-external-provisioner nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner --set nfs.server=192.168.110.101 --set nfs.path=/data/nfs --set storageClass.defaultClass=true -n kube-system # 2、查看 helm -n kube-system list # 3、查看nfs_provider的pod kubectl -n kube-system get pods |grep nfs nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-797c875548-rt4dh 1/1 Running 2 (58m ago) 23h # 4、查看sc(已经设置为默认的了) kubectl -n kube-system get sc nfs-client NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE nfs-client (default) cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner Delete Immediate true 23h 二、添加仓库地址helm repo add harbor https://helm.goharbor.io helm repo list三、下载Chart包到本地因为需要修改的参数比较多,在命令行直接helm install比较复杂,我就将Chart包下载到本地,再修改一些配置,这样比较直观,也比较符合实际工作中的业务环境。helm pull harbor/harbor # 下载Chart包 tar zxvf harbor-1.14.2.tgz # 解压包四、修改values.yamlexpose: # Set how to expose the service. Set the type as "ingress", "clusterIP", "nodePort" or "loadBalancer" # and fill the information in the corresponding section type: nodePort tls: # Enable TLS or not. # Delete the "ssl-redirect" annotations in "expose.ingress.annotations" when TLS is disabled and "expose.type" is "ingress" # Note: if the "expose.type" is "ingress" and TLS is disabled, # the port must be included in the command when pulling/pushing images. # Refer to https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/5291 for details. enabled: false # The source of the tls certificate. Set as "auto", "secret" # or "none" and fill the information in the corresponding section # 1) auto: generate the tls certificate automatically # 2) secret: read the tls certificate from the specified secret. # The tls certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager # 3) none: configure no tls certificate for the ingress. If the default # tls certificate is configured in the ingress controller, choose this option certSource: auto auto: # The common name used to generate the certificate, it's necessary # when the type isn't "ingress" commonName: "" secret: # The name of secret which contains keys named: # "tls.crt" - the certificate # "tls.key" - the private key secretName: "" ingress: hosts: core: core.harbor.domain # set to the type of ingress controller if it has specific requirements. # leave as `default` for most ingress controllers. # set to `gce` if using the GCE ingress controller # set to `ncp` if using the NCP (NSX-T Container Plugin) ingress controller # set to `alb` if using the ALB ingress controller # set to `f5-bigip` if using the F5 BIG-IP ingress controller controller: default ## Allow .Capabilities.KubeVersion.Version to be overridden while creating ingress kubeVersionOverride: "" className: "" annotations: # note different ingress controllers may require a different ssl-redirect annotation # for Envoy, use ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "true" and remove the nginx lines below ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true" ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "0" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "0" # ingress-specific labels labels: {} clusterIP: # The name of ClusterIP service name: harbor # The ip address of the ClusterIP service (leave empty for acquiring dynamic ip) staticClusterIP: "" ports: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP httpPort: 80 # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS httpsPort: 443 # Annotations on the ClusterIP service annotations: {} # ClusterIP-specific labels labels: {} nodePort: # The name of NodePort service name: harbor ports: http: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP port: 80 # The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP nodePort: 30002 https: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS port: 443 # The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS nodePort: 30003 # Annotations on the nodePort service annotations: {} # nodePort-specific labels labels: {} loadBalancer: # The name of LoadBalancer service name: harbor # Set the IP if the LoadBalancer supports assigning IP IP: "" ports: # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP httpPort: 80 # The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS httpsPort: 443 # Annotations on the loadBalancer service annotations: {} # loadBalancer-specific labels labels: {} sourceRanges: [] # The external URL for Harbor core service. It is used to # 1) populate the docker/helm commands showed on portal # 2) populate the token service URL returned to docker client # # Format: protocol://domain[:port]. Usually: # 1) if "expose.type" is "ingress", the "domain" should be # the value of "expose.ingress.hosts.core" # 2) if "expose.type" is "clusterIP", the "domain" should be # the value of "expose.clusterIP.name" # 3) if "expose.type" is "nodePort", the "domain" should be # the IP address of k8s node # # If Harbor is deployed behind the proxy, set it as the URL of proxy externalURL: http://192.168.110.101:30002 # The persistence is enabled by default and a default StorageClass # is needed in the k8s cluster to provision volumes dynamically. # Specify another StorageClass in the "storageClass" or set "existingClaim" # if you already have existing persistent volumes to use # # For storing images and charts, you can also use "azure", "gcs", "s3", # "swift" or "oss". Set it in the "imageChartStorage" section persistence: enabled: true # Setting it to "keep" to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete # operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart deleted # (this does not apply for PVCs that are created for internal database # and redis components, i.e. they are never deleted automatically) resourcePolicy: "keep" persistentVolumeClaim: registry: # Use the existing PVC which must be created manually before bound, # and specify the "subPath" if the PVC is shared with other components existingClaim: "" # Specify the "storageClass" used to provision the volume. Or the default # StorageClass will be used (the default). # Set it to "-" to disable dynamic provisioning storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 5Gi annotations: {} jobservice: jobLog: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi annotations: {} # If external database is used, the following settings for database will # be ignored database: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi annotations: {} # If external Redis is used, the following settings for Redis will # be ignored redis: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "nfs-client" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi annotations: {} trivy: existingClaim: "" storageClass: "" subPath: "" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 5Gi annotations: {} # Define which storage backend is used for registry to store # images and charts. Refer to # https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/main/docs/content/about/configuration.md#storage # for the detail. imageChartStorage: # Specify whether to disable `redirect` for images and chart storage, for # backends which not supported it (such as using minio for `s3` storage type), please disable # it. To disable redirects, simply set `disableredirect` to `true` instead. # Refer to # https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/main/docs/configuration.md#redirect # for the detail. disableredirect: false # Specify the "caBundleSecretName" if the storage service uses a self-signed certificate. # The secret must contain keys named "ca.crt" which will be injected into the trust store # of registry's containers. # caBundleSecretName: # Specify the type of storage: "filesystem", "azure", "gcs", "s3", "swift", # "oss" and fill the information needed in the corresponding section. The type # must be "filesystem" if you want to use persistent volumes for registry type: filesystem filesystem: rootdirectory: /storage #maxthreads: 100 azure: accountname: accountname accountkey: base64encodedaccountkey container: containername #realm: core.windows.net # To use existing secret, the key must be AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY existingSecret: "" gcs: bucket: bucketname # The base64 encoded json file which contains the key encodedkey: base64-encoded-json-key-file #rootdirectory: /gcs/object/name/prefix #chunksize: "5242880" # To use existing secret, the key must be GCS_KEY_DATA existingSecret: "" useWorkloadIdentity: false s3: # Set an existing secret for S3 accesskey and secretkey # keys in the secret should be REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_ACCESSKEY and REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_SECRETKEY for registry #existingSecret: "" region: us-west-1 bucket: bucketname #accesskey: awsaccesskey #secretkey: awssecretkey #regionendpoint: http://myobjects.local #encrypt: false #keyid: mykeyid #secure: true #skipverify: false #v4auth: true #chunksize: "5242880" #rootdirectory: /s3/object/name/prefix #storageclass: STANDARD #multipartcopychunksize: "33554432" #multipartcopymaxconcurrency: 100 #multipartcopythresholdsize: "33554432" swift: authurl: https://storage.myprovider.com/v3/auth username: username password: password container: containername # keys in existing secret must be REGISTRY_STORAGE_SWIFT_PASSWORD, REGISTRY_STORAGE_SWIFT_SECRETKEY, REGISTRY_STORAGE_SWIFT_ACCESSKEY existingSecret: "" #region: fr #tenant: tenantname #tenantid: tenantid #domain: domainname #domainid: domainid #trustid: trustid #insecureskipverify: false #chunksize: 5M #prefix: #secretkey: secretkey #accesskey: accesskey #authversion: 3 #endpointtype: public #tempurlcontainerkey: false #tempurlmethods: oss: accesskeyid: accesskeyid accesskeysecret: accesskeysecret region: regionname bucket: bucketname # key in existingSecret must be REGISTRY_STORAGE_OSS_ACCESSKEYSECRET existingSecret: "" #endpoint: endpoint #internal: false #encrypt: false #secure: true #chunksize: 10M #rootdirectory: rootdirectory # The initial password of Harbor admin. Change it from portal after launching Harbor # or give an existing secret for it # key in secret is given via (default to HARBOR_ADMIN_PASSWORD) # existingSecretAdminPassword: existingSecretAdminPasswordKey: HARBOR_ADMIN_PASSWORD harborAdminPassword: "Harbor12345" # The internal TLS used for harbor components secure communicating. In order to enable https # in each component tls cert files need to provided in advance. internalTLS: # If internal TLS enabled enabled: false # enable strong ssl ciphers (default: false) strong_ssl_ciphers: false # There are three ways to provide tls # 1) "auto" will generate cert automatically # 2) "manual" need provide cert file manually in following value # 3) "secret" internal certificates from secret certSource: "auto" # The content of trust ca, only available when `certSource` is "manual" trustCa: "" # core related cert configuration core: # secret name for core's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of core's TLS cert file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of core's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # jobservice related cert configuration jobservice: # secret name for jobservice's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of jobservice's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of jobservice's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # registry related cert configuration registry: # secret name for registry's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of registry's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of registry's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # portal related cert configuration portal: # secret name for portal's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of portal's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of portal's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" # trivy related cert configuration trivy: # secret name for trivy's tls certs secretName: "" # Content of trivy's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" crt: "" # Content of trivy's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual" key: "" ipFamily: # ipv6Enabled set to true if ipv6 is enabled in cluster, currently it affected the nginx related component ipv6: enabled: true # ipv4Enabled set to true if ipv4 is enabled in cluster, currently it affected the nginx related component ipv4: enabled: true imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent # Use this set to assign a list of default pullSecrets imagePullSecrets: # - name: docker-registry-secret # - name: internal-registry-secret # The update strategy for deployments with persistent volumes(jobservice, registry): "RollingUpdate" or "Recreate" # Set it as "Recreate" when "RWM" for volumes isn't supported updateStrategy: type: RollingUpdate # debug, info, warning, error or fatal logLevel: info # The name of the secret which contains key named "ca.crt". Setting this enables the # download link on portal to download the CA certificate when the certificate isn't # generated automatically caSecretName: "" # The secret key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars. secretKey: "not-a-secure-key" # If using existingSecretSecretKey, the key must be secretKey existingSecretSecretKey: "" # The proxy settings for updating trivy vulnerabilities from the Internet and replicating # artifacts from/to the registries that cannot be reached directly proxy: httpProxy: httpsProxy: noProxy: 127.0.0.1,localhost,.local,.internal components: - core - jobservice - trivy # Run the migration job via helm hook enableMigrateHelmHook: false # The custom ca bundle secret, the secret must contain key named "ca.crt" # which will be injected into the trust store for core, jobservice, registry, trivy components # caBundleSecretName: "" ## UAA Authentication Options # If you're using UAA for authentication behind a self-signed # certificate you will need to provide the CA Cert. # Set uaaSecretName below to provide a pre-created secret that # contains a base64 encoded CA Certificate named `ca.crt`. # uaaSecretName: metrics: enabled: true core: path: /metrics port: 8001 registry: path: /metrics port: 8001 jobservice: path: /metrics port: 8001 exporter: path: /metrics port: 8001 ## Create prometheus serviceMonitor to scrape harbor metrics. ## This requires the monitoring.coreos.com/v1 CRD. Please see ## https://github.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/blob/main/Documentation/user-guides/getting-started.md ## serviceMonitor: enabled: false additionalLabels: {} # Scrape interval. If not set, the Prometheus default scrape interval is used. interval: "" # Metric relabel configs to apply to samples before ingestion. metricRelabelings: [] # - action: keep # regex: 'kube_(daemonset|deployment|pod|namespace|node|statefulset).+' # sourceLabels: [__name__] # Relabel configs to apply to samples before ingestion. relabelings: [] # - sourceLabels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] # separator: ; # regex: ^(.*)$ # targetLabel: nodename # replacement: $1 # action: replace trace: enabled: false # trace provider: jaeger or otel # jaeger should be 1.26+ provider: jaeger # set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth sample_rate: 1 # namespace used to differentiate different harbor services # namespace: # attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider # attributes: # application: harbor jaeger: # jaeger supports two modes: # collector mode(uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed) # agent mode(uncomment agent_host and agent_port) endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces # username: # password: # agent_host: hostname # export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode # agent_port: 6831 otel: endpoint: hostname:4318 url_path: /v1/traces compression: false insecure: true # timeout is in seconds timeout: 10 # cache layer configurations # if this feature enabled, harbor will cache the resource # `project/project_metadata/repository/artifact/manifest` in the redis # which help to improve the performance of high concurrent pulling manifest. cache: # default is not enabled. enabled: false # default keep cache for one day. expireHours: 24 ## set Container Security Context to comply with PSP restricted policy if necessary ## each of the conatiner will apply the same security context ## containerSecurityContext:{} is initially an empty yaml that you could edit it on demand, we just filled with a common template for convenience containerSecurityContext: privileged: false allowPrivilegeEscalation: false seccompProfile: type: RuntimeDefault runAsNonRoot: true capabilities: drop: - ALL # If service exposed via "ingress", the Nginx will not be used nginx: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/nginx-photon tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: portal: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/harbor-portal tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## Additional service annotations serviceAnnotations: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] core: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/harbor-core tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 ## Startup probe values startupProbe: enabled: true initialDelaySeconds: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## Additional service annotations serviceAnnotations: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] ## User settings configuration json string configureUserSettings: # The provider for updating project quota(usage), there are 2 options, redis or db. # By default it is implemented by db but you can configure it to redis which # can improve the performance of high concurrent pushing to the same project, # and reduce the database connections spike and occupies. # Using redis will bring up some delay for quota usage updation for display, so only # suggest switch provider to redis if you were ran into the db connections spike around # the scenario of high concurrent pushing to same project, no improvment for other scenes. quotaUpdateProvider: db # Or redis # Secret is used when core server communicates with other components. # If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one. Alternatively set existingSecret to use an existing secret # Must be a string of 16 chars. secret: "" # Fill in the name of a kubernetes secret if you want to use your own # If using existingSecret, the key must be secret existingSecret: "" # Fill the name of a kubernetes secret if you want to use your own # TLS certificate and private key for token encryption/decryption. # The secret must contain keys named: # "tls.key" - the private key # "tls.crt" - the certificate secretName: "" # If not specifying a preexisting secret, a secret can be created from tokenKey and tokenCert and used instead. # If none of secretName, tokenKey, and tokenCert are specified, an ephemeral key and certificate will be autogenerated. # tokenKey and tokenCert must BOTH be set or BOTH unset. # The tokenKey value is formatted as a multiline string containing a PEM-encoded RSA key, indented one more than tokenKey on the following line. tokenKey: | # If tokenKey is set, the value of tokenCert must be set as a PEM-encoded certificate signed by tokenKey, and supplied as a multiline string, indented one more than tokenCert on the following line. tokenCert: | # The XSRF key. Will be generated automatically if it isn't specified xsrfKey: "" # If using existingSecret, the key is defined by core.existingXsrfSecretKey existingXsrfSecret: "" # If using existingSecret, the key existingXsrfSecretKey: CSRF_KEY # The time duration for async update artifact pull_time and repository # pull_count, the unit is second. Will be 10 seconds if it isn't set. # eg. artifactPullAsyncFlushDuration: 10 artifactPullAsyncFlushDuration: gdpr: deleteUser: false auditLogsCompliant: false jobservice: image: repository: goharbor/harbor-jobservice tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] maxJobWorkers: 10 # The logger for jobs: "file", "database" or "stdout" jobLoggers: - file # - database # - stdout # The jobLogger sweeper duration (ignored if `jobLogger` is `stdout`) loggerSweeperDuration: 14 #days notification: webhook_job_max_retry: 3 webhook_job_http_client_timeout: 3 # in seconds reaper: # the max time to wait for a task to finish, if unfinished after max_update_hours, the task will be mark as error, but the task will continue to run, default value is 24 max_update_hours: 24 # the max time for execution in running state without new task created max_dangling_hours: 168 # Secret is used when job service communicates with other components. # If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one. # Must be a string of 16 chars. secret: "" # Use an existing secret resource existingSecret: "" # Key within the existing secret for the job service secret existingSecretKey: JOBSERVICE_SECRET registry: registry: image: repository: goharbor/registry-photon tag: v2.11.1 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] controller: image: repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/harbor-registryctl tag: v2.11.1 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # Secret is used to secure the upload state from client # and registry storage backend. # See: https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/main/docs/configuration.md#http # If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one. # Must be a string of 16 chars. secret: "" # Use an existing secret resource existingSecret: "" # Key within the existing secret for the registry service secret existingSecretKey: REGISTRY_HTTP_SECRET # If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL. relativeurls: false credentials: username: "harbor_registry_user" password: "harbor_registry_password" # If using existingSecret, the key must be REGISTRY_PASSWD and REGISTRY_HTPASSWD existingSecret: "" # Login and password in htpasswd string format. Excludes `registry.credentials.username` and `registry.credentials.password`. May come in handy when integrating with tools like argocd or flux. This allows the same line to be generated each time the template is rendered, instead of the `htpasswd` function from helm, which generates different lines each time because of the salt. # htpasswdString: $apr1$XLefHzeG$Xl4.s00sMSCCcMyJljSZb0 # example string htpasswdString: "" middleware: enabled: false type: cloudFront cloudFront: baseurl: example.cloudfront.net keypairid: KEYPAIRID duration: 3000s ipfilteredby: none # The secret key that should be present is CLOUDFRONT_KEY_DATA, which should be the encoded private key # that allows access to CloudFront privateKeySecret: "my-secret" # enable purge _upload directories upload_purging: enabled: true # remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week. age: 168h # the interval of the purge operations interval: 24h dryrun: false trivy: # enabled the flag to enable Trivy scanner enabled: true image: # repository the repository for Trivy adapter image repository: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/adapter-photon # tag the tag for Trivy adapter image tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false # replicas the number of Pod replicas replicas: 1 resources: requests: cpu: 200m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 1 memory: 1Gi extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # debugMode the flag to enable Trivy debug mode with more verbose scanning log debugMode: false # vulnType a comma-separated list of vulnerability types. Possible values are `os` and `library`. vulnType: "os,library" # severity a comma-separated list of severities to be checked severity: "UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL" # ignoreUnfixed the flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities ignoreUnfixed: false # insecure the flag to skip verifying registry certificate insecure: false # gitHubToken the GitHub access token to download Trivy DB # # Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases. # It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached # in the local file system (`/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db/trivy.db`). In addition, the database contains the update # timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. # Currently, the database is updated every 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub. # # Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough # for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000 # requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult # https://developer.github.com/v3/#rate-limiting # # You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in # https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line gitHubToken: "" # skipUpdate the flag to disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub # # You might want to set the value of this flag to `true` in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues. # If the value is set to `true` you have to manually download the `trivy.db` file and mount it in the # `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db/trivy.db` path. skipUpdate: false # skipJavaDBUpdate If the flag is enabled you have to manually download the `trivy-java.db` file and mount it in the # `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/java-db/trivy-java.db` path # skipJavaDBUpdate: false # The offlineScan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. # # Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it. # For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't # exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode. # It would work if all the dependencies are in local. # This option doesn’t affect DB download. You need to specify skipUpdate as well as offlineScan in an air-gapped environment. offlineScan: false # Comma-separated list of what security issues to detect. Possible values are `vuln`, `config` and `secret`. Defaults to `vuln`. securityCheck: "vuln" # The duration to wait for scan completion timeout: 5m0s database: # if external database is used, set "type" to "external" # and fill the connection information in "external" section type: internal internal: image: repository: goharbor/harbor-db tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m # The timeout used in livenessProbe; 1 to 5 seconds livenessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 1 # The timeout used in readinessProbe; 1 to 5 seconds readinessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 1 extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. extrInitContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # The initial superuser password for internal database password: "changeit" # The size limit for Shared memory, pgSQL use it for shared_buffer # More details see: # https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/15034 shmSizeLimit: 512Mi initContainer: migrator: {} # resources: # requests: # memory: 128Mi # cpu: 100m permissions: {} # resources: # requests: # memory: 128Mi # cpu: 100m external: host: "192.168.0.1" port: "5432" username: "user" password: "password" coreDatabase: "registry" # if using existing secret, the key must be "password" existingSecret: "" # "disable" - No SSL # "require" - Always SSL (skip verification) # "verify-ca" - Always SSL (verify that the certificate presented by the # server was signed by a trusted CA) # "verify-full" - Always SSL (verify that the certification presented by the # server was signed by a trusted CA and the server host name matches the one # in the certificate) sslmode: "disable" # The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool per pod (core+exporter). # If it <=0, no idle connections are retained. maxIdleConns: 100 # The maximum number of open connections to the database per pod (core+exporter). # If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections. # Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for harbor's postgres. maxOpenConns: 900 ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} redis: # if external Redis is used, set "type" to "external" # and fill the connection information in "external" section type: internal internal: image: repository: goharbor/redis-photon tag: v2.11.1 # set the service account to be used, default if left empty serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # containers to be run before the controller's container starts. initContainers: [] # Example: # # - name: wait # image: busybox # command: [ 'sh', '-c', "sleep 20" ] # # jobserviceDatabaseIndex defaults to "1" # # registryDatabaseIndex defaults to "2" # # trivyAdapterIndex defaults to "5" # # harborDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "6", this config is optional # # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "7", this config is optional jobserviceDatabaseIndex: "1" registryDatabaseIndex: "2" trivyAdapterIndex: "5" # harborDatabaseIndex: "6" # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex: "7" external: # support redis, redis+sentinel # addr for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis> # addr for redis+sentinel: <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3> addr: "192.168.0.2:6379" # The name of the set of Redis instances to monitor, it must be set to support redis+sentinel sentinelMasterSet: "" # The "coreDatabaseIndex" must be "0" as the library Harbor # used doesn't support configuring it # harborDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "6", this config is optional # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex defaults to "0", but it can be configured to "7", this config is optional coreDatabaseIndex: "0" jobserviceDatabaseIndex: "1" registryDatabaseIndex: "2" trivyAdapterIndex: "5" # harborDatabaseIndex: "6" # cacheLayerDatabaseIndex: "7" # username field can be an empty string, and it will be authenticated against the default user username: "" password: "" # If using existingSecret, the key must be REDIS_PASSWORD existingSecret: "" ## Additional deployment annotations podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} exporter: image: repository: goharbor/harbor-exporter tag: v2.11.1 serviceAccountName: "" # mount the service account token automountServiceAccountToken: false replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 # resources: # requests: # memory: 256Mi # cpu: 100m extraEnvVars: [] podAnnotations: {} ## Additional deployment labels podLabels: {} nodeSelector: {} tolerations: [] affinity: {} # Spread Pods across failure-domains like regions, availability zones or nodes topologySpreadConstraints: [] ## The priority class to run the pod as priorityClassName: # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # nodeTaintsPolicy: Honor # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule cacheDuration: 23 cacheCleanInterval: 14400 五、安装kubectl create namespace harbor helm install harbor . -n harbor # 将安装资源部署到harbor命名空间 # 注意 # 1、部署过程可能因为下载镜像慢导致redis尚未启动成功,其他pod会出现启动失败的现象,耐心等一会即可 # 2、如果下载速度过慢,可以自己制作镜像,或者下载镜像后上传到服务器导入 # nerdctl -n k8s.io load -i xxxxxxxxxxx.tar六、查看[root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 0/1 Running 2 (66s ago) 3m21s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (79s ago) 3m21s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 5 (6s ago) 3m21s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 3m21s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 0/1 Running 2 (77s ago) 3m32s harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (78s ago) 3m33s ^C[root@master01 harbor]# ^C [root@master01 harbor]# ^C [root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor delete pod harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26 & [1] 103883 [root@master01 harbor]# pod "harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26" deleted [1]+ 完成 kubectl -n harbor delete pod harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-8wb26 [root@master01 harbor]# [root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (2m13s ago) 4m28s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (2m26s ago) 4m28s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 0/1 Running 0 6s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 4m28s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 4m28s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m28s ^C[root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (2m26s ago) 4m41s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (2m39s ago) 4m41s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 0/1 Running 0 19s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 4m41s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m41s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 1/1 Running 0 21s ^C[root@master01 harbor]# ^C [root@master01 harbor]# kubectl -n harbor get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE harbor-core-586f48cb4c-4r7gz 1/1 Running 2 (2m31s ago) 4m46s harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-exporter-74ff648dfc-k6pb2 1/1 Running 2 (2m44s ago) 4m46s harbor-jobservice-864b5bc9b9-vkr6w 1/1 Running 0 24s harbor-nginx-6c5fc7c744-5m9lz 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-portal-74484f87f5-lh8m6 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 4m46s harbor-registry-b7f8d77d6-ltpw7 2/2 Running 0 4m46s harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 4m46s七、登录http://192.168.110.101:30002,账号:admin 密码:Harbor12345 -
 altertmanager邮件报警+对接钉钉 一、配置altertmanager二进制包下载地址:https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/releases/ 官方文档: https://prometheus.io/docs/alerting/configuration/ 一个报警信息在生命周期内有下面 3 种状态`pending`: 当某个监控指标触发了告警表达式的条件,但还没有持续足够长的时间,即没有超过 `for` 阈值设定的时间,这个告警状态被标记为 `pending` `firing`: 当某个监控指标触发了告警条件并且持续超过了设定的 `for` 时间,告警将由pending状态改成 `firing`。 Prometheus 在 firing 状态下将告警信息发送至 Alertmanager。 Alertmanager 应用路由规则,将通知发送给配置的接收器,例如邮件。 `inactive`: 当某个监控指标不再满足告警条件或者告警从未被触发时,这个告警状态被标记为 `inactive`3种状态转换流程 初始状态:`inactive` - 内存使用率正常,告警处于 `inactive` 状态。 expr设置的条件首次满足: - 内存使用率首次超过 20%,告警状态变为 `pending`。 2分钟内情况: - 如果内存使用率在超过 20% 的状态下持续了2分钟或以上,告警状态从 `pending` 变为 `firing`。 - 如果内存使用率在2分钟内恢复正常,状态从 `pending` 变回 `inactive`。解压以后直接kubectl apply -f alertmanager.yml[root@master01 ddd]# tar xf alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz [root@master01 ddd]# ls alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz [root@master01 ddd]# cd alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64/ [root@master01 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64]# ls alertmanager alertmanager.yml amtool LICENSE NOTICE [root@master01 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64]# vi alertmanager [root@master01 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64]# vi alertmanager.yml 配置文件[root@master01 test]# cat altertmanager.yaml # alertmanager-config.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: alert-config namespace: monitor data: template_email.tmpl: |- {{ define "email.html" }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Firing) 0 -}} @报警<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>概述:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>详情:</strong> {{ .Annotations.description }}<br> <strong>时间:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Resolved) 0 -}} @恢复<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>信息:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>恢复:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{ end }} config.yml: |- templates: # 1、增加 templates 配置,指定模板文件 - '/etc/alertmanager/template_email.tmpl' inhibit_rules: - source_match: # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则1产生的所有报警信息都带着下面2个标签,第一个标签是promethus自动添加,第二个使我们自己加的 alertname: NodeMemoryUsage severity: critical target_match: severity: normal # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则2产生的所有报警信息都带着该标签 equal: - instance # instance是每条报警规则自带的标签,值为对应的节点名 # 一、全局配置 global: # (1)当alertmanager持续多长时间未接收到告警后标记告警状态为 resolved(解决了) resolve_timeout: 5m # (2)配置发邮件的邮箱 smtp_smarthost: 'smtp.163.com:25' smtp_from: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_username: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_password: 'PZJWYQLDCKQGTTKZ' # 填入你开启pop3时获得的码 smtp_hello: '163.com' smtp_require_tls: false # 二、设置报警的路由分发策略 route: # 定义用于告警分组的标签。当有多个告警消息有相同的 alertname 和 cluster 标签时,这些告警消息将会被聚合到同一个分组中 # 例如,接收到的报警信息里面有许多具有 cluster=XXX 和 alertname=YYY 这样的标签的报警信息将会批量被聚合到一个分组里面 group_by: ['alertname', 'cluster'] # 当一个新的报警分组被创建后,需要等待至少 group_wait 时间来初始化通知, # 这种方式可以确保您能有足够的时间为同一分组来获取/累积多个警报,然后一起触发这个报警信息。 group_wait: 30s # 短期聚合: group_interval 确保在短时间内,同一分组的多个告警将会合并/聚合到一起等待被发送,避免过于频繁的告警通知。 group_interval: 30s # 长期提醒: repeat_interval确保长时间未解决的告警不会被遗忘,Alertmanager每隔一段时间定期提醒相关人员,直到告警被解决。 repeat_interval: 120s # 实验环境想快速看下效果,可以缩小该时间,比如设置为120s # 上述两个参数的综合解释: #(1)当一个新的告警被触发时,会立即发送初次通知 #(2)然后开始一个 group_interval 窗口(例如 30 秒)。 # 在 group_interval 窗口内,任何新的同分组告警会被聚合到一起,但不会立即触发发送。 #(3)聚合窗口结束后, # 如果刚好抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,聚合的告警会和原有未解决的告警一起发送通知。 # 如果没有抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,则原有未解决的报警不会重复发送,直到到达下一个 repeat_interval 时间点。 # 这两个参数一起工作,确保短时间内的警报状态变化不会造成过多的重复通知,同时在长期未解决的情况下提供定期的提醒。 # 默认的receiver:如果一个报警没有被一个route匹配,则发送给默认的接收器,与下面receivers中定义的name呼应 receiver: default routes: # 子路由规则。子路由继承父路由的所有属性,可以进行覆盖和更具体的规则匹配。 - receiver: email # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 continue: true #不设置这个只能匹配一条 - receiver: mywebhook # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 # 三、定义接收器,与上面的路由定义中引用的介receiver相呼应 receivers: - name: 'default' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 email_configs: - to: '7902731@qq.com@qq.com' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 - name: 'email' # 名为 email 的接收器配置,与之前定义的子路由相对应。 email_configs: - to: '15555519627@163.com' send_resolved: true html: '{{ template "email.html" . }}' #这个是对接webhook钉钉的 - name: 'mywebhook' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 webhook_configs: - url: 'http://promoter:8080/dingtalk/webhook1/send' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 --- # alertmanager-deploy.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: matchLabels: app: alertmanager template: metadata: labels: app: alertmanager spec: volumes: - name: alertcfg configMap: name: alert-config containers: - name: alertmanager # 版本去查看官网https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/releases/ # 1、官网镜像地址,需要你为containerd配置好镜像加速 #image: prom/alertmanager:v0.27.0 # 2、搞成了国内的地址 image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/egon-k8s-test/alertmanager:v0.27.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent args: - '--config.file=/etc/alertmanager/config.yml' ports: - containerPort: 9093 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: '/etc/alertmanager' name: alertcfg resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi --- # alertmanager-svc.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: app: alertmanager type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9093 targetPort: http [root@master01 test]# kubectl -n monitor get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE alertmanager NodePort 10.99.103.160 <none> 9093:30610/TCP 107m grafana NodePort 10.99.18.224 <none> 3000:30484/TCP 28h prometheus NodePort 10.108.206.132 <none> 9090:31119/TCP 3d1h promoter ClusterIP 10.97.213.227 <none> 8080/TCP 18h redis ClusterIP 10.97.184.21 <none> 6379/TCP,9121/TCP 2d22h [root@master01 test]# kubectl -n monitor get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE alertmanager-56b46ff6b4-mvbb8 1/1 Running 0 125m grafana-86cfcd87fb-59gtb 1/1 Running 1 (3h25m ago) 28h node-exporter-6f4d4 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h node-exporter-swr5j 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h node-exporter-tf84v 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h node-exporter-z9svr 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h prometheus-7f8f87f55d-zbnsr 1/1 Running 1 (3h25m ago) 21h promoter-6f68cff456-wqmg9 1/1 Running 1 (3h25m ago) 18h redis-84bbc5df9b-rnm6q 2/2 Running 8 (3h25m ago) 2d22h 基于webhook对接钉钉报警 prometheus(报警规则)----》alertmanager组件-----------------------------》邮箱 prometheus(报警规则)----》alertmanager组件------钉钉的webhook软件------》钉钉{lamp/}二、配置钉钉1.下载钉钉 2.添加群聊(至少2个人才可以拉群) 3.在群里添加机器人得道AIP接口和密钥测试是否可以正常使用#python 3.8 import time import sys import hmac import hashlib import base64 import urllib.parse import requests timestamp = str(round(time.time() * 1000)) secret = 'SEC45045323ac8b379b88e04750c7954645edc54c4ffdedd717b82804c8684c0706' secret_enc = secret.encode('utf-8') string_to_sign = '{}\n{}'.format(timestamp, secret) string_to_sign_enc = string_to_sign.encode('utf-8') hmac_code = hmac.new(secret_enc, string_to_sign_enc, digestmod=hashlib.sha256).digest() sign = urllib.parse.quote_plus(base64.b64encode(hmac_code)) print(timestamp) print(sign) MESSAGE = sys.argv[1] webhook_url =f'https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=13ddb964c0108de8b56eb944c5e407d448cb2db02e3885c45585f8eb06779def×tamp={timestamp}&sign={sign}' response = requests.post(webhook_url,headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'},json={"msgtype": "text","text": {"content":f"'{MESSAGE}'"}}) print(response.text) print(response.status_code)pip3 install requests -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ python3 webhook_test.py 测试部署钉钉的webhook软件wget https://github.com/timonwong/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/releases/download/v2.1.0/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk-2.1.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz #解压出来里面的config.yml配置 cat > /usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/config.yml << "EOF" templates: - /etc/template.tmpl targets: webhook1: url: https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=3acdac2167b83e0b54f751c0cfcbb676b7828af183aca2e21428c489883ced8b # secret for signature secret: SEC67f8b6d15997deaf686ab0509b2dad943aca99d700131f88d010ef57e591aea0 message: # 哪个target需要引用模版,就增加这一小段配置,其中default.tmpl就是你一会要定义的模版 text: '{{ template "default.tmpl" . }}' # 可以添加其他的对接,主要用于对接到不同的群中的机器人 webhook_mention_all: url: https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=3acdac2167b83e0b54f751c0cfcbb676b7828af183aca2e21428c489883ced8b secret: SEC67f8b6d15997deaf686ab0509b2dad943aca99d700131f88d010ef57e591aea0 mention: all: true webhook_mention_users: url: https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=3acdac2167b83e0b54f751c0cfcbb676b7828af183aca2e21428c489883ced8b secret: SEC67f8b6d15997deaf686ab0509b2dad943aca99d700131f88d010ef57e591aea0 mention: mobiles: ['18611453110'] EOF可以做成系统服务cat > /lib/systemd/system/dingtalk.service << 'EOF' [Unit] Description=dingtalk Documentation=https://github.com/timonwong/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/ After=network.target [Service] Restart=on-failure WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk ExecStart=/usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:8060 --config.file=/usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/config.yml User=nobody [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart dingtalk systemctl status dingtalk配置alertmanager对接钉钉webhook[root@master01 test]# cat altertmanager.yaml # alertmanager-config.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: alert-config namespace: monitor data: template_email.tmpl: |- {{ define "email.html" }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Firing) 0 -}} @报警<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>概述:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>详情:</strong> {{ .Annotations.description }}<br> <strong>时间:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Resolved) 0 -}} @恢复<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>信息:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>恢复:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{ end }} config.yml: |- templates: # 1、增加 templates 配置,指定模板文件 - '/etc/alertmanager/template_email.tmpl' inhibit_rules: - source_match: # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则1产生的所有报警信息都带着下面2个标签,第一个标签是promethus自动添加,第二个使我们自己加的 alertname: NodeMemoryUsage severity: critical target_match: severity: normal # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则2产生的所有报警信息都带着该标签 equal: - instance # instance是每条报警规则自带的标签,值为对应的节点名 # 一、全局配置 global: # (1)当alertmanager持续多长时间未接收到告警后标记告警状态为 resolved(解决了) resolve_timeout: 5m # (2)配置发邮件的邮箱 smtp_smarthost: 'smtp.163.com:25' smtp_from: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_username: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_password: 'PZJWYQLDCKQGTTKZ' # 填入你开启pop3时获得的码 smtp_hello: '163.com' smtp_require_tls: false # 二、设置报警的路由分发策略 route: # 定义用于告警分组的标签。当有多个告警消息有相同的 alertname 和 cluster 标签时,这些告警消息将会被聚合到同一个分组中 # 例如,接收到的报警信息里面有许多具有 cluster=XXX 和 alertname=YYY 这样的标签的报警信息将会批量被聚合到一个分组里面 group_by: ['alertname', 'cluster'] # 当一个新的报警分组被创建后,需要等待至少 group_wait 时间来初始化通知, # 这种方式可以确保您能有足够的时间为同一分组来获取/累积多个警报,然后一起触发这个报警信息。 group_wait: 30s # 短期聚合: group_interval 确保在短时间内,同一分组的多个告警将会合并/聚合到一起等待被发送,避免过于频繁的告警通知。 group_interval: 30s # 长期提醒: repeat_interval确保长时间未解决的告警不会被遗忘,Alertmanager每隔一段时间定期提醒相关人员,直到告警被解决。 repeat_interval: 120s # 实验环境想快速看下效果,可以缩小该时间,比如设置为120s # 上述两个参数的综合解释: #(1)当一个新的告警被触发时,会立即发送初次通知 #(2)然后开始一个 group_interval 窗口(例如 30 秒)。 # 在 group_interval 窗口内,任何新的同分组告警会被聚合到一起,但不会立即触发发送。 #(3)聚合窗口结束后, # 如果刚好抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,聚合的告警会和原有未解决的告警一起发送通知。 # 如果没有抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,则原有未解决的报警不会重复发送,直到到达下一个 repeat_interval 时间点。 # 这两个参数一起工作,确保短时间内的警报状态变化不会造成过多的重复通知,同时在长期未解决的情况下提供定期的提醒。 # 默认的receiver:如果一个报警没有被一个route匹配,则发送给默认的接收器,与下面receivers中定义的name呼应 receiver: default routes: # 子路由规则。子路由继承父路由的所有属性,可以进行覆盖和更具体的规则匹配。 - receiver: email # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 continue: true #不设置这个只能匹配一条 - receiver: mywebhook # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 # 三、定义接收器,与上面的路由定义中引用的介receiver相呼应 receivers: - name: 'default' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 email_configs: - to: '7902731@qq.com@qq.com' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 - name: 'email' # 名为 email 的接收器配置,与之前定义的子路由相对应。 email_configs: - to: '15555519627@163.com' send_resolved: true html: '{{ template "email.html" . }}' #这个是对接webhook钉钉的 - name: 'mywebhook' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 webhook_configs: - url: 'http://promoter:8080/dingtalk/webhook1/send' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 --- # alertmanager-deploy.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: matchLabels: app: alertmanager template: metadata: labels: app: alertmanager spec: volumes: - name: alertcfg configMap: name: alert-config containers: - name: alertmanager # 版本去查看官网https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/releases/ # 1、官网镜像地址,需要你为containerd配置好镜像加速 #image: prom/alertmanager:v0.27.0 # 2、搞成了国内的地址 image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/egon-k8s-test/alertmanager:v0.27.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent args: - '--config.file=/etc/alertmanager/config.yml' ports: - containerPort: 9093 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: '/etc/alertmanager' name: alertcfg resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi --- # alertmanager-svc.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: app: alertmanager type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9093 targetPort: http 补充:报警图片 https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing1.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing2.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing3.png https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing4.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing5.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing6.png 定制内容(略) 自行研究吧:https://github.com/timonwong/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/blob/main/template/default.tmpl
altertmanager邮件报警+对接钉钉 一、配置altertmanager二进制包下载地址:https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/releases/ 官方文档: https://prometheus.io/docs/alerting/configuration/ 一个报警信息在生命周期内有下面 3 种状态`pending`: 当某个监控指标触发了告警表达式的条件,但还没有持续足够长的时间,即没有超过 `for` 阈值设定的时间,这个告警状态被标记为 `pending` `firing`: 当某个监控指标触发了告警条件并且持续超过了设定的 `for` 时间,告警将由pending状态改成 `firing`。 Prometheus 在 firing 状态下将告警信息发送至 Alertmanager。 Alertmanager 应用路由规则,将通知发送给配置的接收器,例如邮件。 `inactive`: 当某个监控指标不再满足告警条件或者告警从未被触发时,这个告警状态被标记为 `inactive`3种状态转换流程 初始状态:`inactive` - 内存使用率正常,告警处于 `inactive` 状态。 expr设置的条件首次满足: - 内存使用率首次超过 20%,告警状态变为 `pending`。 2分钟内情况: - 如果内存使用率在超过 20% 的状态下持续了2分钟或以上,告警状态从 `pending` 变为 `firing`。 - 如果内存使用率在2分钟内恢复正常,状态从 `pending` 变回 `inactive`。解压以后直接kubectl apply -f alertmanager.yml[root@master01 ddd]# tar xf alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz [root@master01 ddd]# ls alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz [root@master01 ddd]# cd alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64/ [root@master01 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64]# ls alertmanager alertmanager.yml amtool LICENSE NOTICE [root@master01 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64]# vi alertmanager [root@master01 alertmanager-0.27.0.linux-amd64]# vi alertmanager.yml 配置文件[root@master01 test]# cat altertmanager.yaml # alertmanager-config.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: alert-config namespace: monitor data: template_email.tmpl: |- {{ define "email.html" }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Firing) 0 -}} @报警<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>概述:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>详情:</strong> {{ .Annotations.description }}<br> <strong>时间:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Resolved) 0 -}} @恢复<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>信息:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>恢复:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{ end }} config.yml: |- templates: # 1、增加 templates 配置,指定模板文件 - '/etc/alertmanager/template_email.tmpl' inhibit_rules: - source_match: # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则1产生的所有报警信息都带着下面2个标签,第一个标签是promethus自动添加,第二个使我们自己加的 alertname: NodeMemoryUsage severity: critical target_match: severity: normal # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则2产生的所有报警信息都带着该标签 equal: - instance # instance是每条报警规则自带的标签,值为对应的节点名 # 一、全局配置 global: # (1)当alertmanager持续多长时间未接收到告警后标记告警状态为 resolved(解决了) resolve_timeout: 5m # (2)配置发邮件的邮箱 smtp_smarthost: 'smtp.163.com:25' smtp_from: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_username: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_password: 'PZJWYQLDCKQGTTKZ' # 填入你开启pop3时获得的码 smtp_hello: '163.com' smtp_require_tls: false # 二、设置报警的路由分发策略 route: # 定义用于告警分组的标签。当有多个告警消息有相同的 alertname 和 cluster 标签时,这些告警消息将会被聚合到同一个分组中 # 例如,接收到的报警信息里面有许多具有 cluster=XXX 和 alertname=YYY 这样的标签的报警信息将会批量被聚合到一个分组里面 group_by: ['alertname', 'cluster'] # 当一个新的报警分组被创建后,需要等待至少 group_wait 时间来初始化通知, # 这种方式可以确保您能有足够的时间为同一分组来获取/累积多个警报,然后一起触发这个报警信息。 group_wait: 30s # 短期聚合: group_interval 确保在短时间内,同一分组的多个告警将会合并/聚合到一起等待被发送,避免过于频繁的告警通知。 group_interval: 30s # 长期提醒: repeat_interval确保长时间未解决的告警不会被遗忘,Alertmanager每隔一段时间定期提醒相关人员,直到告警被解决。 repeat_interval: 120s # 实验环境想快速看下效果,可以缩小该时间,比如设置为120s # 上述两个参数的综合解释: #(1)当一个新的告警被触发时,会立即发送初次通知 #(2)然后开始一个 group_interval 窗口(例如 30 秒)。 # 在 group_interval 窗口内,任何新的同分组告警会被聚合到一起,但不会立即触发发送。 #(3)聚合窗口结束后, # 如果刚好抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,聚合的告警会和原有未解决的告警一起发送通知。 # 如果没有抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,则原有未解决的报警不会重复发送,直到到达下一个 repeat_interval 时间点。 # 这两个参数一起工作,确保短时间内的警报状态变化不会造成过多的重复通知,同时在长期未解决的情况下提供定期的提醒。 # 默认的receiver:如果一个报警没有被一个route匹配,则发送给默认的接收器,与下面receivers中定义的name呼应 receiver: default routes: # 子路由规则。子路由继承父路由的所有属性,可以进行覆盖和更具体的规则匹配。 - receiver: email # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 continue: true #不设置这个只能匹配一条 - receiver: mywebhook # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 # 三、定义接收器,与上面的路由定义中引用的介receiver相呼应 receivers: - name: 'default' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 email_configs: - to: '7902731@qq.com@qq.com' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 - name: 'email' # 名为 email 的接收器配置,与之前定义的子路由相对应。 email_configs: - to: '15555519627@163.com' send_resolved: true html: '{{ template "email.html" . }}' #这个是对接webhook钉钉的 - name: 'mywebhook' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 webhook_configs: - url: 'http://promoter:8080/dingtalk/webhook1/send' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 --- # alertmanager-deploy.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: matchLabels: app: alertmanager template: metadata: labels: app: alertmanager spec: volumes: - name: alertcfg configMap: name: alert-config containers: - name: alertmanager # 版本去查看官网https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/releases/ # 1、官网镜像地址,需要你为containerd配置好镜像加速 #image: prom/alertmanager:v0.27.0 # 2、搞成了国内的地址 image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/egon-k8s-test/alertmanager:v0.27.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent args: - '--config.file=/etc/alertmanager/config.yml' ports: - containerPort: 9093 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: '/etc/alertmanager' name: alertcfg resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi --- # alertmanager-svc.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: app: alertmanager type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9093 targetPort: http [root@master01 test]# kubectl -n monitor get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE alertmanager NodePort 10.99.103.160 <none> 9093:30610/TCP 107m grafana NodePort 10.99.18.224 <none> 3000:30484/TCP 28h prometheus NodePort 10.108.206.132 <none> 9090:31119/TCP 3d1h promoter ClusterIP 10.97.213.227 <none> 8080/TCP 18h redis ClusterIP 10.97.184.21 <none> 6379/TCP,9121/TCP 2d22h [root@master01 test]# kubectl -n monitor get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE alertmanager-56b46ff6b4-mvbb8 1/1 Running 0 125m grafana-86cfcd87fb-59gtb 1/1 Running 1 (3h25m ago) 28h node-exporter-6f4d4 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h node-exporter-swr5j 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h node-exporter-tf84v 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h node-exporter-z9svr 1/1 Running 4 (3h25m ago) 2d21h prometheus-7f8f87f55d-zbnsr 1/1 Running 1 (3h25m ago) 21h promoter-6f68cff456-wqmg9 1/1 Running 1 (3h25m ago) 18h redis-84bbc5df9b-rnm6q 2/2 Running 8 (3h25m ago) 2d22h 基于webhook对接钉钉报警 prometheus(报警规则)----》alertmanager组件-----------------------------》邮箱 prometheus(报警规则)----》alertmanager组件------钉钉的webhook软件------》钉钉{lamp/}二、配置钉钉1.下载钉钉 2.添加群聊(至少2个人才可以拉群) 3.在群里添加机器人得道AIP接口和密钥测试是否可以正常使用#python 3.8 import time import sys import hmac import hashlib import base64 import urllib.parse import requests timestamp = str(round(time.time() * 1000)) secret = 'SEC45045323ac8b379b88e04750c7954645edc54c4ffdedd717b82804c8684c0706' secret_enc = secret.encode('utf-8') string_to_sign = '{}\n{}'.format(timestamp, secret) string_to_sign_enc = string_to_sign.encode('utf-8') hmac_code = hmac.new(secret_enc, string_to_sign_enc, digestmod=hashlib.sha256).digest() sign = urllib.parse.quote_plus(base64.b64encode(hmac_code)) print(timestamp) print(sign) MESSAGE = sys.argv[1] webhook_url =f'https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=13ddb964c0108de8b56eb944c5e407d448cb2db02e3885c45585f8eb06779def×tamp={timestamp}&sign={sign}' response = requests.post(webhook_url,headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'},json={"msgtype": "text","text": {"content":f"'{MESSAGE}'"}}) print(response.text) print(response.status_code)pip3 install requests -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ python3 webhook_test.py 测试部署钉钉的webhook软件wget https://github.com/timonwong/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/releases/download/v2.1.0/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk-2.1.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz #解压出来里面的config.yml配置 cat > /usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/config.yml << "EOF" templates: - /etc/template.tmpl targets: webhook1: url: https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=3acdac2167b83e0b54f751c0cfcbb676b7828af183aca2e21428c489883ced8b # secret for signature secret: SEC67f8b6d15997deaf686ab0509b2dad943aca99d700131f88d010ef57e591aea0 message: # 哪个target需要引用模版,就增加这一小段配置,其中default.tmpl就是你一会要定义的模版 text: '{{ template "default.tmpl" . }}' # 可以添加其他的对接,主要用于对接到不同的群中的机器人 webhook_mention_all: url: https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=3acdac2167b83e0b54f751c0cfcbb676b7828af183aca2e21428c489883ced8b secret: SEC67f8b6d15997deaf686ab0509b2dad943aca99d700131f88d010ef57e591aea0 mention: all: true webhook_mention_users: url: https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=3acdac2167b83e0b54f751c0cfcbb676b7828af183aca2e21428c489883ced8b secret: SEC67f8b6d15997deaf686ab0509b2dad943aca99d700131f88d010ef57e591aea0 mention: mobiles: ['18611453110'] EOF可以做成系统服务cat > /lib/systemd/system/dingtalk.service << 'EOF' [Unit] Description=dingtalk Documentation=https://github.com/timonwong/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/ After=network.target [Service] Restart=on-failure WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk ExecStart=/usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:8060 --config.file=/usr/local/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/config.yml User=nobody [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart dingtalk systemctl status dingtalk配置alertmanager对接钉钉webhook[root@master01 test]# cat altertmanager.yaml # alertmanager-config.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: alert-config namespace: monitor data: template_email.tmpl: |- {{ define "email.html" }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Firing) 0 -}} @报警<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>概述:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>详情:</strong> {{ .Annotations.description }}<br> <strong>时间:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{- if gt (len .Alerts.Resolved) 0 -}} @恢复<br> {{- range .Alerts }} <strong>实例:</strong> {{ .Labels.instance }}<br> <strong>信息:</strong> {{ .Annotations.summary }}<br> <strong>恢复:</strong> {{ (.StartsAt.Add 28800e9).Format "2006-01-02 15:04:05" }} <br> {{- end -}} {{- end }} {{ end }} config.yml: |- templates: # 1、增加 templates 配置,指定模板文件 - '/etc/alertmanager/template_email.tmpl' inhibit_rules: - source_match: # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则1产生的所有报警信息都带着下面2个标签,第一个标签是promethus自动添加,第二个使我们自己加的 alertname: NodeMemoryUsage severity: critical target_match: severity: normal # prometheus配置文件中的报警规则2产生的所有报警信息都带着该标签 equal: - instance # instance是每条报警规则自带的标签,值为对应的节点名 # 一、全局配置 global: # (1)当alertmanager持续多长时间未接收到告警后标记告警状态为 resolved(解决了) resolve_timeout: 5m # (2)配置发邮件的邮箱 smtp_smarthost: 'smtp.163.com:25' smtp_from: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_username: '15555519627@163.com' smtp_auth_password: 'PZJWYQLDCKQGTTKZ' # 填入你开启pop3时获得的码 smtp_hello: '163.com' smtp_require_tls: false # 二、设置报警的路由分发策略 route: # 定义用于告警分组的标签。当有多个告警消息有相同的 alertname 和 cluster 标签时,这些告警消息将会被聚合到同一个分组中 # 例如,接收到的报警信息里面有许多具有 cluster=XXX 和 alertname=YYY 这样的标签的报警信息将会批量被聚合到一个分组里面 group_by: ['alertname', 'cluster'] # 当一个新的报警分组被创建后,需要等待至少 group_wait 时间来初始化通知, # 这种方式可以确保您能有足够的时间为同一分组来获取/累积多个警报,然后一起触发这个报警信息。 group_wait: 30s # 短期聚合: group_interval 确保在短时间内,同一分组的多个告警将会合并/聚合到一起等待被发送,避免过于频繁的告警通知。 group_interval: 30s # 长期提醒: repeat_interval确保长时间未解决的告警不会被遗忘,Alertmanager每隔一段时间定期提醒相关人员,直到告警被解决。 repeat_interval: 120s # 实验环境想快速看下效果,可以缩小该时间,比如设置为120s # 上述两个参数的综合解释: #(1)当一个新的告警被触发时,会立即发送初次通知 #(2)然后开始一个 group_interval 窗口(例如 30 秒)。 # 在 group_interval 窗口内,任何新的同分组告警会被聚合到一起,但不会立即触发发送。 #(3)聚合窗口结束后, # 如果刚好抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,聚合的告警会和原有未解决的告警一起发送通知。 # 如果没有抵达 repeat_interval 的时间点,则原有未解决的报警不会重复发送,直到到达下一个 repeat_interval 时间点。 # 这两个参数一起工作,确保短时间内的警报状态变化不会造成过多的重复通知,同时在长期未解决的情况下提供定期的提醒。 # 默认的receiver:如果一个报警没有被一个route匹配,则发送给默认的接收器,与下面receivers中定义的name呼应 receiver: default routes: # 子路由规则。子路由继承父路由的所有属性,可以进行覆盖和更具体的规则匹配。 - receiver: email # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 continue: true #不设置这个只能匹配一条 - receiver: mywebhook # 匹配此子路由的告警将发送到的接收器,该名字也与下面的receivers中定义的name呼应 group_wait: 10s # 等待时间,可覆盖父路由的 group_by: ['instance'] # 根据instance做分组 match: # 告警标签匹配条件,只有匹配到特定条件的告警才会应用该子路由规则。 team: node # 只有拥有 team=node 标签的告警才会路由到 email 接收器。 # 三、定义接收器,与上面的路由定义中引用的介receiver相呼应 receivers: - name: 'default' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 email_configs: - to: '7902731@qq.com@qq.com' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 - name: 'email' # 名为 email 的接收器配置,与之前定义的子路由相对应。 email_configs: - to: '15555519627@163.com' send_resolved: true html: '{{ template "email.html" . }}' #这个是对接webhook钉钉的 - name: 'mywebhook' # 默认接收器配置,未匹配任何特定路由规则的告警会发送到此接收器。 webhook_configs: - url: 'http://promoter:8080/dingtalk/webhook1/send' send_resolved: true # : 当告警恢复时是否也发送通知。 --- # alertmanager-deploy.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: matchLabels: app: alertmanager template: metadata: labels: app: alertmanager spec: volumes: - name: alertcfg configMap: name: alert-config containers: - name: alertmanager # 版本去查看官网https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/releases/ # 1、官网镜像地址,需要你为containerd配置好镜像加速 #image: prom/alertmanager:v0.27.0 # 2、搞成了国内的地址 image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/egon-k8s-test/alertmanager:v0.27.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent args: - '--config.file=/etc/alertmanager/config.yml' ports: - containerPort: 9093 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: '/etc/alertmanager' name: alertcfg resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi --- # alertmanager-svc.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: alertmanager namespace: monitor labels: app: alertmanager spec: selector: app: alertmanager type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9093 targetPort: http 补充:报警图片 https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing1.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing2.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing3.png https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing4.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing5.jpg https://egonimages.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/gaojing6.png 定制内容(略) 自行研究吧:https://github.com/timonwong/prometheus-webhook-dingtalk/blob/main/template/default.tmpl -
 grafana grafana使用要先做nfs挂载卷[root@master01 test]# kubectl get pv NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE grafana-pv 2Gi RWO Retain Bound monitor/grafana-pvc nfs-client <unset> 27h[root@master01 test]# cat grafana.yaml # grafana.yaml # 为grafana创建持久存储,用于存放插件等数据,挂载到容器的/var/lib/grafana下 apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: grafana-pvc namespace: monitor labels: app: grafana spec: storageClassName: nfs-client accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 2Gi --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: grafana namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: grafana template: metadata: labels: app: grafana spec: volumes: - name: storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: grafana-pvc securityContext: runAsUser: 0 # 必须以root身份运行 containers: - name: grafana image: grafana/grafana # 默认lastest最新,也可以指定版本grafana/grafana:10.4.4 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent ports: - containerPort: 3000 name: grafana env: # 配置 grafana 的管理员用户和密码的, - name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER value: admin - name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD value: admin321 readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 10 httpGet: path: /api/health port: 3000 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 30 livenessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 httpGet: path: /api/health port: 3000 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 1 resources: limits: cpu: 150m memory: 512Mi requests: cpu: 150m memory: 512Mi volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/grafana name: storage --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: grafana namespace: monitor spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 3000 selector: app: grafana [root@master01 /]# kubectl -n monitor get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE alertmanager NodePort 10.99.103.160 <none> 9093:30610/TCP 94m grafana NodePort 10.99.18.224 <none> 3000:30484/TCP 28h prometheus NodePort 10.108.206.132 <none> 9090:31119/TCP 3d1h promoter ClusterIP 10.97.213.227 <none> 8080/TCP 18h redis ClusterIP 10.97.184.21 <none> 6379/TCP,9121/TCP 2d21h 使用grafana出图先使用浏览器访问<你的物理机IP地址>:(1)添加仪表图形(2)选择对接的监控(3)设置需要对接的IP+端口(其他不用修改)(4)添加图形模板(5)查看已经配置好的
grafana grafana使用要先做nfs挂载卷[root@master01 test]# kubectl get pv NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE grafana-pv 2Gi RWO Retain Bound monitor/grafana-pvc nfs-client <unset> 27h[root@master01 test]# cat grafana.yaml # grafana.yaml # 为grafana创建持久存储,用于存放插件等数据,挂载到容器的/var/lib/grafana下 apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: grafana-pvc namespace: monitor labels: app: grafana spec: storageClassName: nfs-client accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 2Gi --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: grafana namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: grafana template: metadata: labels: app: grafana spec: volumes: - name: storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: grafana-pvc securityContext: runAsUser: 0 # 必须以root身份运行 containers: - name: grafana image: grafana/grafana # 默认lastest最新,也可以指定版本grafana/grafana:10.4.4 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent ports: - containerPort: 3000 name: grafana env: # 配置 grafana 的管理员用户和密码的, - name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER value: admin - name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD value: admin321 readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 10 httpGet: path: /api/health port: 3000 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 30 livenessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 httpGet: path: /api/health port: 3000 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 1 resources: limits: cpu: 150m memory: 512Mi requests: cpu: 150m memory: 512Mi volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/grafana name: storage --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: grafana namespace: monitor spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 3000 selector: app: grafana [root@master01 /]# kubectl -n monitor get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE alertmanager NodePort 10.99.103.160 <none> 9093:30610/TCP 94m grafana NodePort 10.99.18.224 <none> 3000:30484/TCP 28h prometheus NodePort 10.108.206.132 <none> 9090:31119/TCP 3d1h promoter ClusterIP 10.97.213.227 <none> 8080/TCP 18h redis ClusterIP 10.97.184.21 <none> 6379/TCP,9121/TCP 2d21h 使用grafana出图先使用浏览器访问<你的物理机IP地址>:(1)添加仪表图形(2)选择对接的监控(3)设置需要对接的IP+端口(其他不用修改)(4)添加图形模板(5)查看已经配置好的 -
 监控k8s 抓取apiserver的监控指标 - job_name: 'kubernetes-apiservers' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace,__meta_kubernetes_service_name,__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] # 把符合要求的保留下来 action: keep regex: default;kubernetes;https抓取kube-controller-manager的监控指标 # 1、创建svc,标签选择选中, apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/component: kube-controller-manager app.kubernetes.io/name: kube-controller-manager k8s-app: kube-controller-manager name: kube-controller-manager namespace: kube-system spec: clusterIP: None ports: - name: https-metrics port: 10257 targetPort: 10257 protocol: TCP selector: component: kube-controller-manager # 2、你可以查看下上述svc其关联的endpoint用的地址都是物理机的地址,而每台机器上的controller-manager都监听在127.0.0.1,所以是无法访问的,需要修改其默认监听 vi /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml # 修改--bind-address=127.0.0.1 每台master节点都改 # 3、添加监控 - job_name: 'kube-controller-manager' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace,__meta_kubernetes_service_name,__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] action: keep regex: kube-system;kube-controller-manager;https-metrics # 这里的https-metrics名字与你svc中为ports起的名字保持一致 抓取kube-scheduler的监控指标 同上 抓取etcd的监控指标 # 1、修改每个master节点上etcd的静态配置yaml - --listen-metrics-urls=http://127.0.0.1:2381 # 2、etcd-service.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: namespace: kube-system name: etcd labels: k8s-app: etcd spec: selector: component: etcd type: ClusterIP clusterIP: None ports: - name: http port: 2381 targetPort: 2381 protocol: TCP # 3、etcd监控 - job_name: 'etcd' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints scheme: http relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] action: keep regex: kube-system;etcd;http 自动发现业务服务 - job_name: 'kubernetes-endpoints' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints relabel_configs: # 1、匹配元数据__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape包含"true"的留下 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true # 2、__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme的值中包含0或1个https,则改名为__scheme__ - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace target_label: __scheme__ regex: (https?) # 3、__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path的值至少有一个任意字符,则改名为__metrics_path__ - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 4、提取ip与port拼接到一起格式为: 1.1.1.1:3333,然后赋值给新label名:__address__ - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) # RE2 正则规则,+是一次多多次,?是0次或1次,其中?:表示非匹>配组(意思就是不获取匹配结果) replacement: $1:$2 # 5、添加标签 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) # 6、名称空间标签替换为kubernetes_namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_namespace # 7、服务名替换为kubernetes_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_name # 8、pod名替换为kubernetes_pod_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_pod_name 自动发现测试 # prome-redis.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: redis template: metadata: labels: app: redis spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:4 resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 6379 - name: redis-exporter image: oliver006/redis_exporter:latest resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 9121 --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor annotations: # --------------------------------》 添加 prometheus.io/scrape: 'true' prometheus.io/port: '9121' spec: selector: app: redis ports: - name: redis port: 6379 targetPort: 6379 - name: prom port: 9121 targetPort: 9121
监控k8s 抓取apiserver的监控指标 - job_name: 'kubernetes-apiservers' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace,__meta_kubernetes_service_name,__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] # 把符合要求的保留下来 action: keep regex: default;kubernetes;https抓取kube-controller-manager的监控指标 # 1、创建svc,标签选择选中, apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/component: kube-controller-manager app.kubernetes.io/name: kube-controller-manager k8s-app: kube-controller-manager name: kube-controller-manager namespace: kube-system spec: clusterIP: None ports: - name: https-metrics port: 10257 targetPort: 10257 protocol: TCP selector: component: kube-controller-manager # 2、你可以查看下上述svc其关联的endpoint用的地址都是物理机的地址,而每台机器上的controller-manager都监听在127.0.0.1,所以是无法访问的,需要修改其默认监听 vi /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml # 修改--bind-address=127.0.0.1 每台master节点都改 # 3、添加监控 - job_name: 'kube-controller-manager' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace,__meta_kubernetes_service_name,__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] action: keep regex: kube-system;kube-controller-manager;https-metrics # 这里的https-metrics名字与你svc中为ports起的名字保持一致 抓取kube-scheduler的监控指标 同上 抓取etcd的监控指标 # 1、修改每个master节点上etcd的静态配置yaml - --listen-metrics-urls=http://127.0.0.1:2381 # 2、etcd-service.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: namespace: kube-system name: etcd labels: k8s-app: etcd spec: selector: component: etcd type: ClusterIP clusterIP: None ports: - name: http port: 2381 targetPort: 2381 protocol: TCP # 3、etcd监控 - job_name: 'etcd' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints scheme: http relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] action: keep regex: kube-system;etcd;http 自动发现业务服务 - job_name: 'kubernetes-endpoints' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints relabel_configs: # 1、匹配元数据__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape包含"true"的留下 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true # 2、__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme的值中包含0或1个https,则改名为__scheme__ - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace target_label: __scheme__ regex: (https?) # 3、__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path的值至少有一个任意字符,则改名为__metrics_path__ - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 4、提取ip与port拼接到一起格式为: 1.1.1.1:3333,然后赋值给新label名:__address__ - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) # RE2 正则规则,+是一次多多次,?是0次或1次,其中?:表示非匹>配组(意思就是不获取匹配结果) replacement: $1:$2 # 5、添加标签 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) # 6、名称空间标签替换为kubernetes_namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_namespace # 7、服务名替换为kubernetes_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_name # 8、pod名替换为kubernetes_pod_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_pod_name 自动发现测试 # prome-redis.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: redis template: metadata: labels: app: redis spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:4 resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 6379 - name: redis-exporter image: oliver006/redis_exporter:latest resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 9121 --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor annotations: # --------------------------------》 添加 prometheus.io/scrape: 'true' prometheus.io/port: '9121' spec: selector: app: redis ports: - name: redis port: 6379 targetPort: 6379 - name: prom port: 9121 targetPort: 9121 -
 prometheus部署 一、 二进制安装prometheus server 物理机直接部署下载最新版二进制包见:https://prometheus.io/download , 下载历史版本见:https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/tags LTS: 2.53.x版 注意:最新版本的prometheus,可能会出现grafana上模板没有数据,不兼容的新规则的问题 ========================================》二进制安装prometheus server # 1、先做个软连接方便后续升级 ln -s /monitor/prometheus-2.53.0.linux-amd64 /monitor/prometheus mkdir /monitor/prometheus/data # 创建tsdb数据目录 # 2、添加系统服务 cat > /usr/lib/systemd/system/prometheus.service << 'EOF' [Unit] Description=prometheus server daemon [Service] Restart=on-failure ExecStart=/monitor/prometheus/prometheus --config.file=/monitor/prometheus/prometheus.yml --storage.tsdb.path=/monitor/prometheus/data --storage.tsdb.retention.time=30d --web.enable-lifecycle [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF # 3、启动 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable prometheus.service systemctl start prometheus.service systemctl status prometheus netstat -tunalp |grep 9090测试下载并构建测试程序,作为被监控者,对外暴漏了/metrics接口 yum install golang -y git clone https://github.com/prometheus/client_golang.git cd client_golang/examples/random export GO111MODULE=on export GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn go build # 得到一个二进制命令random 然后在 3 个独立的终端里面运行 3 个服务: ./random -listen-address=:8080 # 对外暴漏http://localhost:8080/metrics ./random -listen-address=:8081 # 对外暴漏http://localhost:8081/metrics ./random -listen-address=:8082 # 对外暴漏http://localhost:8080/metrics 因为都对外暴漏了/metrics接口,并且数据格式遵循prometheus规范,所以我们可以在prometheus.yml中添加监控项假设8080与8081是生产实例,8082是金丝雀实例,那么我们放到不同的target里然后用标签区分,配置如下 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'example-random' # Override the global default and scrape targets from this job every 5 seconds. scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8080', '192.168.110.101:8081'] labels: group: 'production' - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8082'] labels: group: 'canary'systemctl restart prometheus 然后查看页面http://192.168.110.101:9090/ 点击Status---》Targets,发现有新增的监控job二、 安装prometheus server到k8s#prometheus-cm.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: prometheus-config namespace: monitor data: prometheus.yml: | global: scrape_interval: 15s # Prometheus每隔15s就会从所有配置的目标端点抓取最新的数据 scrape_timeout: 15s # 某个抓取操作在 15 秒内未完成,会被视为超时,不会包含在最新的数据中。 evaluation_interval: 15s # # 每15s对告警规则进行计算 scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] prometheus-pv-pvc.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: prometheus-local labels: app: prometheus spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce capacity: storage: 20Gi storageClassName: local-storage local: path: /data/k8s/prometheus nodeAffinity: required: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - master01 persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: prometheus-data namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: prometheus accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 20Gi storageClassName: local-storageprometheus-rbac.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitor --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: prometheus rules: - apiGroups: - '' resources: - nodes - services - endpoints - pods - nodes/proxy verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - 'extensions' resources: - ingresses verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - '' resources: - configmaps - nodes/metrics verbs: - get - nonResourceURLs: # 用来对非资源型 metrics 进行操作的权限声明 - /metrics verbs: - get --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: prometheus roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole # 由于我们要获取的资源信息,在每一个 namespace 下面都有可能存在,所以我们这里使用的是 ClusterRole 的资源对象 name: prometheus subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: prometheus namespace: monitor prometheus-deploy.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitor labels: app: prometheus spec: selector: matchLabels: app: prometheus template: metadata: labels: app: prometheus spec: serviceAccountName: prometheus securityContext: # 确保这里的缩进使用的是空格 runAsUser: 0 containers: - image: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/oooo:1.0 name: prometheus args: - '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml' - '--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus' - '--storage.tsdb.retention.time=24h' - '--web.enable-admin-api' - '--web.enable-lifecycle' ports: - containerPort: 9090 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: '/etc/prometheus' name: config-volume - mountPath: '/prometheus' name: data resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 512Mi volumes: - name: data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: prometheus-data - name: config-volume configMap: name: prometheus-config prometheus-svc.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitor labels: app: prometheus spec: selector: app: prometheus type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9090 targetPort: 9090 #targetPort: http kubectl create namespace monitor kubectl apply -f cm.yaml mkdir /data/k8s/prometheus # 在pv所亲和的节点上创建 kubectl apply -f pv-pvc.yaml kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml kubectl apply -f deploy.yaml kubectl apply -f svc.yaml # 把二进制的停掉 systemctl stop prometheus systemctl disable prometheus # 添加监控项,然后apply -f [root@master01 monitor]# cat prometheus-cm.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: prometheus-config namespace: monitor data: prometheus.yml: | global: scrape_interval: 15s # Prometheus 每隔 15 秒从所有配置的目标端点抓取最新的数据 scrape_timeout: 15s # 某个抓取操作在 15 秒内未完成,会被视为超时,不会包含在最新的数据中。 evaluation_interval: 15s # 每 15 秒对告警规则进行计算 scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] - job_name: 'example-random' scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8080', '192.168.110.101:8081'] labels: group: 'production' - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8082'] labels: group: 'canary' #重载服务 [root@master01 monitor]# kubectl -n monitor get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES prometheus-7b644bfcfc-l5twf 1/1 Running 0 5h25m 10.244.0.18 master01 <none> <none> [root@master01 monitor]# curl -X POST "http://10.108.206.132:9090/-/reload"三、监控应用软件(1)服务自带/metrics接口,直接监控,在配置中增加下述target,然后apply -f - job_name: "coredns" static_configs: - targets: ["kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local:9153"] 等一会后 curl -X POST "http://10.108.206.132:9090/-/reload"(2)应用软件没有自带自带/metrics接口,需要安装对应的exporterexporter官网地址:https://prometheus.io/docs/instrumenting/exporters/ 安装redis yum install redis -y sed -ri 's/bind 127.0.0.1/bind 0.0.0.0/g' /etc/redis.conf sed -ri 's/port 6379/port 16379/g' /etc/redis.conf cat >> /etc/redis.conf << "EOF" requirepass 123456 EOF systemctl restart redis systemctl status redis 添加redis_exporter来采集redis的监控信息 wget https://github.com/oliver006/redis_exporter/releases/download/v1.61.0/redis_exporter-v1.61.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz # 2、安装 tar xf redis_exporter-v1.61.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz mv redis_exporter-v1.61.0.linux-amd64/redis_exporter /usr/bin/ # 3、制作系统服务 cat > /usr/lib/systemd/system/redis_exporter.service << 'EOF' [Unit] Description=Redis Exporter Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target [Service] User=root Group=root Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/bin/redis_exporter --redis.addr=redis://127.0.0.1:16379 --redis.password=123456 --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9122 --exclude-latency-histogram-metrics [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF #4、启动 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart redis_exporter systemctl status redis_exporter # 5、在cm中增加监控项目 - job_name: "redis-server" # 添加这一条 static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.71.101:9122"] kubectl apply -f prometheus-cm.yaml # 6、过一会后,执行prometheus server的reload curl -X POST "http://10.108.206.132:9090/-/reload" # 7、补充说明 如果你的redis-server跑在k8s中,那我们通常不会像上面一样裸部署一个redis_exporter,而是会以`sidecar` 的形式将redis_exporter和主应用redis_server部署在同一个 Pod 中,如下所示 # prome-redis.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: redis template: metadata: labels: app: redis spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:4 resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 6379 - name: redis-exporter image: oliver006/redis_exporter:latest resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 9121 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor spec: selector: app: redis ports: - name: redis port: 6379 targetPort: 6379 - name: prom port: 9121 targetPort: 9121 # 然后你就可以用该svc的clusterip结合9121端口来访问/metrics接口 # curl 上面的svc的clusterip地址:9121/metrics # 添加监控项,直接用svc名字即可, 更新prometheus-cm.yaml 的配置文件如下 - job_name: 'redis' static_configs: - targets: ['redis:9121']
prometheus部署 一、 二进制安装prometheus server 物理机直接部署下载最新版二进制包见:https://prometheus.io/download , 下载历史版本见:https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/tags LTS: 2.53.x版 注意:最新版本的prometheus,可能会出现grafana上模板没有数据,不兼容的新规则的问题 ========================================》二进制安装prometheus server # 1、先做个软连接方便后续升级 ln -s /monitor/prometheus-2.53.0.linux-amd64 /monitor/prometheus mkdir /monitor/prometheus/data # 创建tsdb数据目录 # 2、添加系统服务 cat > /usr/lib/systemd/system/prometheus.service << 'EOF' [Unit] Description=prometheus server daemon [Service] Restart=on-failure ExecStart=/monitor/prometheus/prometheus --config.file=/monitor/prometheus/prometheus.yml --storage.tsdb.path=/monitor/prometheus/data --storage.tsdb.retention.time=30d --web.enable-lifecycle [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF # 3、启动 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable prometheus.service systemctl start prometheus.service systemctl status prometheus netstat -tunalp |grep 9090测试下载并构建测试程序,作为被监控者,对外暴漏了/metrics接口 yum install golang -y git clone https://github.com/prometheus/client_golang.git cd client_golang/examples/random export GO111MODULE=on export GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn go build # 得到一个二进制命令random 然后在 3 个独立的终端里面运行 3 个服务: ./random -listen-address=:8080 # 对外暴漏http://localhost:8080/metrics ./random -listen-address=:8081 # 对外暴漏http://localhost:8081/metrics ./random -listen-address=:8082 # 对外暴漏http://localhost:8080/metrics 因为都对外暴漏了/metrics接口,并且数据格式遵循prometheus规范,所以我们可以在prometheus.yml中添加监控项假设8080与8081是生产实例,8082是金丝雀实例,那么我们放到不同的target里然后用标签区分,配置如下 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'example-random' # Override the global default and scrape targets from this job every 5 seconds. scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8080', '192.168.110.101:8081'] labels: group: 'production' - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8082'] labels: group: 'canary'systemctl restart prometheus 然后查看页面http://192.168.110.101:9090/ 点击Status---》Targets,发现有新增的监控job二、 安装prometheus server到k8s#prometheus-cm.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: prometheus-config namespace: monitor data: prometheus.yml: | global: scrape_interval: 15s # Prometheus每隔15s就会从所有配置的目标端点抓取最新的数据 scrape_timeout: 15s # 某个抓取操作在 15 秒内未完成,会被视为超时,不会包含在最新的数据中。 evaluation_interval: 15s # # 每15s对告警规则进行计算 scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] prometheus-pv-pvc.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: prometheus-local labels: app: prometheus spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce capacity: storage: 20Gi storageClassName: local-storage local: path: /data/k8s/prometheus nodeAffinity: required: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - master01 persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: prometheus-data namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: prometheus accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 20Gi storageClassName: local-storageprometheus-rbac.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitor --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: prometheus rules: - apiGroups: - '' resources: - nodes - services - endpoints - pods - nodes/proxy verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - 'extensions' resources: - ingresses verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - '' resources: - configmaps - nodes/metrics verbs: - get - nonResourceURLs: # 用来对非资源型 metrics 进行操作的权限声明 - /metrics verbs: - get --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: prometheus roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole # 由于我们要获取的资源信息,在每一个 namespace 下面都有可能存在,所以我们这里使用的是 ClusterRole 的资源对象 name: prometheus subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: prometheus namespace: monitor prometheus-deploy.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitor labels: app: prometheus spec: selector: matchLabels: app: prometheus template: metadata: labels: app: prometheus spec: serviceAccountName: prometheus securityContext: # 确保这里的缩进使用的是空格 runAsUser: 0 containers: - image: registry.cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xingcangku/oooo:1.0 name: prometheus args: - '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml' - '--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus' - '--storage.tsdb.retention.time=24h' - '--web.enable-admin-api' - '--web.enable-lifecycle' ports: - containerPort: 9090 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: '/etc/prometheus' name: config-volume - mountPath: '/prometheus' name: data resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 512Mi volumes: - name: data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: prometheus-data - name: config-volume configMap: name: prometheus-config prometheus-svc.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitor labels: app: prometheus spec: selector: app: prometheus type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9090 targetPort: 9090 #targetPort: http kubectl create namespace monitor kubectl apply -f cm.yaml mkdir /data/k8s/prometheus # 在pv所亲和的节点上创建 kubectl apply -f pv-pvc.yaml kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml kubectl apply -f deploy.yaml kubectl apply -f svc.yaml # 把二进制的停掉 systemctl stop prometheus systemctl disable prometheus # 添加监控项,然后apply -f [root@master01 monitor]# cat prometheus-cm.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: prometheus-config namespace: monitor data: prometheus.yml: | global: scrape_interval: 15s # Prometheus 每隔 15 秒从所有配置的目标端点抓取最新的数据 scrape_timeout: 15s # 某个抓取操作在 15 秒内未完成,会被视为超时,不会包含在最新的数据中。 evaluation_interval: 15s # 每 15 秒对告警规则进行计算 scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] - job_name: 'example-random' scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8080', '192.168.110.101:8081'] labels: group: 'production' - targets: ['192.168.110.101:8082'] labels: group: 'canary' #重载服务 [root@master01 monitor]# kubectl -n monitor get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES prometheus-7b644bfcfc-l5twf 1/1 Running 0 5h25m 10.244.0.18 master01 <none> <none> [root@master01 monitor]# curl -X POST "http://10.108.206.132:9090/-/reload"三、监控应用软件(1)服务自带/metrics接口,直接监控,在配置中增加下述target,然后apply -f - job_name: "coredns" static_configs: - targets: ["kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local:9153"] 等一会后 curl -X POST "http://10.108.206.132:9090/-/reload"(2)应用软件没有自带自带/metrics接口,需要安装对应的exporterexporter官网地址:https://prometheus.io/docs/instrumenting/exporters/ 安装redis yum install redis -y sed -ri 's/bind 127.0.0.1/bind 0.0.0.0/g' /etc/redis.conf sed -ri 's/port 6379/port 16379/g' /etc/redis.conf cat >> /etc/redis.conf << "EOF" requirepass 123456 EOF systemctl restart redis systemctl status redis 添加redis_exporter来采集redis的监控信息 wget https://github.com/oliver006/redis_exporter/releases/download/v1.61.0/redis_exporter-v1.61.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz # 2、安装 tar xf redis_exporter-v1.61.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz mv redis_exporter-v1.61.0.linux-amd64/redis_exporter /usr/bin/ # 3、制作系统服务 cat > /usr/lib/systemd/system/redis_exporter.service << 'EOF' [Unit] Description=Redis Exporter Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target [Service] User=root Group=root Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/bin/redis_exporter --redis.addr=redis://127.0.0.1:16379 --redis.password=123456 --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9122 --exclude-latency-histogram-metrics [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF #4、启动 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart redis_exporter systemctl status redis_exporter # 5、在cm中增加监控项目 - job_name: "redis-server" # 添加这一条 static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.71.101:9122"] kubectl apply -f prometheus-cm.yaml # 6、过一会后,执行prometheus server的reload curl -X POST "http://10.108.206.132:9090/-/reload" # 7、补充说明 如果你的redis-server跑在k8s中,那我们通常不会像上面一样裸部署一个redis_exporter,而是会以`sidecar` 的形式将redis_exporter和主应用redis_server部署在同一个 Pod 中,如下所示 # prome-redis.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor spec: selector: matchLabels: app: redis template: metadata: labels: app: redis spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:4 resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 6379 - name: redis-exporter image: oliver006/redis_exporter:latest resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 9121 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: redis namespace: monitor spec: selector: app: redis ports: - name: redis port: 6379 targetPort: 6379 - name: prom port: 9121 targetPort: 9121 # 然后你就可以用该svc的clusterip结合9121端口来访问/metrics接口 # curl 上面的svc的clusterip地址:9121/metrics # 添加监控项,直接用svc名字即可, 更新prometheus-cm.yaml 的配置文件如下 - job_name: 'redis' static_configs: - targets: ['redis:9121']