搜索到
93
篇与
的结果
-
 jenkins部署tomcat jenkins部署tomcatmaven编译环境(jenkins服务器) 运行环境(web服务器)一、部署maven编译环境(jenkins)Maven是一个Java项目管理和构建工具,它可以定义项目结构、项目依赖,并使用统一的方式进行自动化构建,是Java项目不可缺少的工具。1.jenkins部署maven软件1.1下载安装包cd /opt wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/apache/maven/maven-3/3.9.9/binaries/apache-maven-3.9.9-bin.tar.gz1.2解压tar -xf apache-maven-3.9.9-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local/1.3配置环境变量[root@master01 opt]# vim /etc/profile.d/maven.sh [root@master01 opt]# cat /etc/profile.d/maven.sh export MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/apache-maven-3.9.9 export PATH=$MAVEN_HOME/bin:$PATH [root@master01 opt]# source /etc/profile [root@master01 opt]# #刷新1.4安装JDK#jenkins安装的时候部署过 [root@master01 opt]# mvn --version Apache Maven 3.9.9 (8e8579a9e76f7d015ee5ec7bfcdc97d260186937) Maven home: /usr/local/apache-maven-3.9.9 Java version: 17.0.0.1, vendor: Oracle Corporation, runtime: /opt/jdk-17.0.0.1 Default locale: zh_CN, platform encoding: UTF-8 OS name: "linux", version: "3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64", arch: "amd64", family: "unix"2.配置jenkins+maven2.1配置JDK2.2配置maven环境变量2.3安装maven插件3.创建代码仓库4.模拟代码上传4.1拉取新仓库[root@master01 opt]# cd /root [root@master01 ~]# git clone git@192.168.3.100:root/tomcat.git 正克隆到 'tomcat'... remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0) 接收对象中: 100% (3/3), done. [root@master01 ~]# cd /tmp/ [root@master01 tmp]# cd /root/tomcat/ [root@master01 tomcat]# ls README.md4.2配置个人信息[root@master01 tomcat]# git config --global user.email "123@qq.com" [root@master01 tomcat]# git config --global user.name "axingkf"4.3模拟代码上传vi javatest.java public class JavaVersion { public static void main(String[] args) { // 打印当前 Java 版本信息 System.out.println("Java Version: " + System.getProperty("java.version")); System.out.println("Java Vendor: " + System.getProperty("java.vendor")); System.out.println("Java Vendor URL: " + System.getProperty("java.vendor.url")); System.out.println("Java Home: " + System.getProperty("java.home")); } }#添加所有文件到暂存区 [root@master01 tomcat]# git add . #提交暂存区的制定文件到仓库区 [root@master01 tomcat]# git commit -m "第一次java开发" [main 51687a7] 第一次java开发 1 file changed, 9 insertions(+) create mode 100644 javatest.java #没有master这个分区 [root@master01 tomcat]# git push -u origin master error: src refspec master does not match any. error: 无法推送一些引用到 'git@192.168.3.100:root/tomcat.git' # 上传到远程 [root@master01 tomcat]# git push -u origin main Counting objects: 4, done. Delta compression using up to 8 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 488 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@192.168.3.100:root/tomcat.git c086be9..51687a7 main -> main 分支 main 设置为跟踪来自 origin 的远程分支 main。 [root@master01 tomcat]# 5、创建maven仓库mkdir -pv /data/software/repository chown jenkins.jenkins /data/software/repository/vim /usr/local/apache-maven-3.6.3/conf/settings.xml #添加本地仓库路径和阿里云镜像 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- | This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels: | | 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user, | and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -s /path/to/user/settings.xml | | 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven | users on a machine (assuming they're all using the same Maven | installation). It's normally provided in | ${maven.conf}/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml | | The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at | getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default | values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided. | |--> <settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.2.0.xsd"> <!-- localRepository --> <localRepository>/data/software/repository</localRepository> <!-- Mirrors --> <mirrors> <!-- Add Aliyun Maven Mirror --> <mirror> <id>aliyun</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <name>Aliyun Maven Mirror</name> <url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public</url> <blocked>false</blocked> </mirror> <mirror> <id>maven-default-http-blocker</id> <mirrorOf>external:http:*</mirrorOf> <name>Pseudo repository to mirror external repositories initially using HTTP.</name> <url>http://0.0.0.0/</url> <blocked>true</blocked> </mirror> </mirrors> <!-- interactiveMode --> <!-- This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false, maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for the parameter in question. --> <!-- <interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode> --> <!-- offline --> <!-- Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build. This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others. --> <!-- <offline>false</offline> --> <!-- pluginGroups --> <pluginGroups> <!-- pluginGroup | Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup. <pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup> --> </pluginGroups> <!-- proxies --> <!-- This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network. Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy specification in this list marked as active will be used. --> <proxies> <!-- proxy | Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network. | <proxy> <id>optional</id> <active>true</active> <protocol>http</protocol> <username>proxyuser</username> <password>proxypass</password> <host>proxy.host.net</host> <port>80</port> <nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts> </proxy> --> </proxies> <!-- servers --> <!-- This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system. Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server. --> <servers> <!-- server | Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by | a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below). | | NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are | used together. | <server> <id>deploymentRepo</id> <username>repouser</username> <password>repopwd</password> </server> --> <!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate. <server> <id>siteServer</id> <privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey> <passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase> </server> --> </servers> <!-- profiles --> <!-- This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine- specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment. --> <profiles> <!-- profile | Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the | mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/> | or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique. | | An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention | for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc. | This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting | to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug. | | This profile --> </profiles> </settings>6、测试maven测试二、部署运行环境1、安装tomcat略2、配置方便启动[Unit] Description=Tomcat 9 After=network.target [Service] Type=forking User=tomcat Group=tomcat Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java/jdk-17.0.0.1 Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/temp/tomcat.pid Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98 Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98 Environment='CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M' ExecStart=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/bin/shutdown.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target访问测试2、修改tomcat监控权限vim /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/conf/tomcat-users.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <tomcat-users xmlns="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml tomcat-users.xsd" version="1.0"> <!-- By default, no user is included in the "manager-gui" role required to operate the "/manager/html" web application. If you wish to use this app, you must define such a user - the username and password are arbitrary. Built-in Tomcat manager roles: - manager-gui - allows access to the HTML GUI and the status pages - manager-script - allows access to the HTTP API and the status pages - manager-jmx - allows access to the JMX proxy and the status pages - manager-status - allows access to the status pages only --> <role rolename="tomcat"/> <role rolename="role1"/> <role rolename="manager-script"/> <role rolename="manager-gui"/> <role rolename="manager-status"/> <role rolename="admin-gui"/> <role rolename="admin-script"/> <user username="tomcat" password="tomcat" roles="manager-gui,manager-script,tomcat,admin-gui,admin-script"/> </tomcat-users> /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <Context antiResourceLocking="false" privileged="true" > <CookieProcessor className="org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Rfc6265CookieProcessor" sameSiteCookies="strict" /> <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve" allow=".*" /> <Manager sessionAttributeValueClassNameFilter="java\.lang\.(?:Boolean|Integer|Long|Number|String)|org\.apache\.catalina\.filters\.CsrfPreventionFilter\$LruCache(?:\$1)?|java\.util\.(?:Linked)?HashMap"/> </Context> systemctl restart tomcat #重启3、配置jenkisn操作tomcat3.1下载部署插件3.2添加凭证3.3部署创建后操作3.4检查3.5jenkins构建记录
jenkins部署tomcat jenkins部署tomcatmaven编译环境(jenkins服务器) 运行环境(web服务器)一、部署maven编译环境(jenkins)Maven是一个Java项目管理和构建工具,它可以定义项目结构、项目依赖,并使用统一的方式进行自动化构建,是Java项目不可缺少的工具。1.jenkins部署maven软件1.1下载安装包cd /opt wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/apache/maven/maven-3/3.9.9/binaries/apache-maven-3.9.9-bin.tar.gz1.2解压tar -xf apache-maven-3.9.9-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local/1.3配置环境变量[root@master01 opt]# vim /etc/profile.d/maven.sh [root@master01 opt]# cat /etc/profile.d/maven.sh export MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/apache-maven-3.9.9 export PATH=$MAVEN_HOME/bin:$PATH [root@master01 opt]# source /etc/profile [root@master01 opt]# #刷新1.4安装JDK#jenkins安装的时候部署过 [root@master01 opt]# mvn --version Apache Maven 3.9.9 (8e8579a9e76f7d015ee5ec7bfcdc97d260186937) Maven home: /usr/local/apache-maven-3.9.9 Java version: 17.0.0.1, vendor: Oracle Corporation, runtime: /opt/jdk-17.0.0.1 Default locale: zh_CN, platform encoding: UTF-8 OS name: "linux", version: "3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64", arch: "amd64", family: "unix"2.配置jenkins+maven2.1配置JDK2.2配置maven环境变量2.3安装maven插件3.创建代码仓库4.模拟代码上传4.1拉取新仓库[root@master01 opt]# cd /root [root@master01 ~]# git clone git@192.168.3.100:root/tomcat.git 正克隆到 'tomcat'... remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0) 接收对象中: 100% (3/3), done. [root@master01 ~]# cd /tmp/ [root@master01 tmp]# cd /root/tomcat/ [root@master01 tomcat]# ls README.md4.2配置个人信息[root@master01 tomcat]# git config --global user.email "123@qq.com" [root@master01 tomcat]# git config --global user.name "axingkf"4.3模拟代码上传vi javatest.java public class JavaVersion { public static void main(String[] args) { // 打印当前 Java 版本信息 System.out.println("Java Version: " + System.getProperty("java.version")); System.out.println("Java Vendor: " + System.getProperty("java.vendor")); System.out.println("Java Vendor URL: " + System.getProperty("java.vendor.url")); System.out.println("Java Home: " + System.getProperty("java.home")); } }#添加所有文件到暂存区 [root@master01 tomcat]# git add . #提交暂存区的制定文件到仓库区 [root@master01 tomcat]# git commit -m "第一次java开发" [main 51687a7] 第一次java开发 1 file changed, 9 insertions(+) create mode 100644 javatest.java #没有master这个分区 [root@master01 tomcat]# git push -u origin master error: src refspec master does not match any. error: 无法推送一些引用到 'git@192.168.3.100:root/tomcat.git' # 上传到远程 [root@master01 tomcat]# git push -u origin main Counting objects: 4, done. Delta compression using up to 8 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 488 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@192.168.3.100:root/tomcat.git c086be9..51687a7 main -> main 分支 main 设置为跟踪来自 origin 的远程分支 main。 [root@master01 tomcat]# 5、创建maven仓库mkdir -pv /data/software/repository chown jenkins.jenkins /data/software/repository/vim /usr/local/apache-maven-3.6.3/conf/settings.xml #添加本地仓库路径和阿里云镜像 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- | This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels: | | 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user, | and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -s /path/to/user/settings.xml | | 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven | users on a machine (assuming they're all using the same Maven | installation). It's normally provided in | ${maven.conf}/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml | | The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at | getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default | values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided. | |--> <settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.2.0.xsd"> <!-- localRepository --> <localRepository>/data/software/repository</localRepository> <!-- Mirrors --> <mirrors> <!-- Add Aliyun Maven Mirror --> <mirror> <id>aliyun</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <name>Aliyun Maven Mirror</name> <url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public</url> <blocked>false</blocked> </mirror> <mirror> <id>maven-default-http-blocker</id> <mirrorOf>external:http:*</mirrorOf> <name>Pseudo repository to mirror external repositories initially using HTTP.</name> <url>http://0.0.0.0/</url> <blocked>true</blocked> </mirror> </mirrors> <!-- interactiveMode --> <!-- This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false, maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for the parameter in question. --> <!-- <interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode> --> <!-- offline --> <!-- Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build. This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others. --> <!-- <offline>false</offline> --> <!-- pluginGroups --> <pluginGroups> <!-- pluginGroup | Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup. <pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup> --> </pluginGroups> <!-- proxies --> <!-- This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network. Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy specification in this list marked as active will be used. --> <proxies> <!-- proxy | Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network. | <proxy> <id>optional</id> <active>true</active> <protocol>http</protocol> <username>proxyuser</username> <password>proxypass</password> <host>proxy.host.net</host> <port>80</port> <nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts> </proxy> --> </proxies> <!-- servers --> <!-- This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system. Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server. --> <servers> <!-- server | Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by | a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below). | | NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are | used together. | <server> <id>deploymentRepo</id> <username>repouser</username> <password>repopwd</password> </server> --> <!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate. <server> <id>siteServer</id> <privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey> <passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase> </server> --> </servers> <!-- profiles --> <!-- This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine- specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment. --> <profiles> <!-- profile | Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the | mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/> | or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique. | | An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention | for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc. | This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting | to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug. | | This profile --> </profiles> </settings>6、测试maven测试二、部署运行环境1、安装tomcat略2、配置方便启动[Unit] Description=Tomcat 9 After=network.target [Service] Type=forking User=tomcat Group=tomcat Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java/jdk-17.0.0.1 Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/temp/tomcat.pid Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98 Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98 Environment='CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M' ExecStart=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/bin/shutdown.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target访问测试2、修改tomcat监控权限vim /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/conf/tomcat-users.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <tomcat-users xmlns="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml tomcat-users.xsd" version="1.0"> <!-- By default, no user is included in the "manager-gui" role required to operate the "/manager/html" web application. If you wish to use this app, you must define such a user - the username and password are arbitrary. Built-in Tomcat manager roles: - manager-gui - allows access to the HTML GUI and the status pages - manager-script - allows access to the HTTP API and the status pages - manager-jmx - allows access to the JMX proxy and the status pages - manager-status - allows access to the status pages only --> <role rolename="tomcat"/> <role rolename="role1"/> <role rolename="manager-script"/> <role rolename="manager-gui"/> <role rolename="manager-status"/> <role rolename="admin-gui"/> <role rolename="admin-script"/> <user username="tomcat" password="tomcat" roles="manager-gui,manager-script,tomcat,admin-gui,admin-script"/> </tomcat-users> /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.98/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <Context antiResourceLocking="false" privileged="true" > <CookieProcessor className="org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Rfc6265CookieProcessor" sameSiteCookies="strict" /> <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve" allow=".*" /> <Manager sessionAttributeValueClassNameFilter="java\.lang\.(?:Boolean|Integer|Long|Number|String)|org\.apache\.catalina\.filters\.CsrfPreventionFilter\$LruCache(?:\$1)?|java\.util\.(?:Linked)?HashMap"/> </Context> systemctl restart tomcat #重启3、配置jenkisn操作tomcat3.1下载部署插件3.2添加凭证3.3部署创建后操作3.4检查3.5jenkins构建记录 -
 jenkins部署PHP 一、架构规划1.gitlab 部署代码仓库 2.jenkins 部署集成工具 3.devops-node 部署nginx、php二、创建代码仓库并编写上传代码1、创建代码仓库2、gitlab添加连接2.1配置ssh秘钥cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub2.2拉取代码仓库git clone git@192.168.3.100:root/php.git #要加上git clone2.3配置个人信息[root@jenkins ~/php]# git config --global user.email "123@qq.com" [root@jenkins ~/php]# git config --global user.name "PHPKF"3、模拟开发编码[root@jenkins ~/php]# echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > index.php # 添加所有文件到暂存区 [root@jenkins ~/php]# git add . # 提交暂存区的指定文件到仓库区 [root@jenkins ~/php]# git commit -m "第一次开发"4、上传本地仓库master文件[root@jenkins ~/php]# git push -u origin master三、jenkins连接业务服务器1、jenkins对业务服务器做ssh免密[root@jenkins ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.3.232、jenkins服务添加业务服务器四、新建项目
jenkins部署PHP 一、架构规划1.gitlab 部署代码仓库 2.jenkins 部署集成工具 3.devops-node 部署nginx、php二、创建代码仓库并编写上传代码1、创建代码仓库2、gitlab添加连接2.1配置ssh秘钥cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub2.2拉取代码仓库git clone git@192.168.3.100:root/php.git #要加上git clone2.3配置个人信息[root@jenkins ~/php]# git config --global user.email "123@qq.com" [root@jenkins ~/php]# git config --global user.name "PHPKF"3、模拟开发编码[root@jenkins ~/php]# echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > index.php # 添加所有文件到暂存区 [root@jenkins ~/php]# git add . # 提交暂存区的指定文件到仓库区 [root@jenkins ~/php]# git commit -m "第一次开发"4、上传本地仓库master文件[root@jenkins ~/php]# git push -u origin master三、jenkins连接业务服务器1、jenkins对业务服务器做ssh免密[root@jenkins ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.3.232、jenkins服务添加业务服务器四、新建项目 -

-
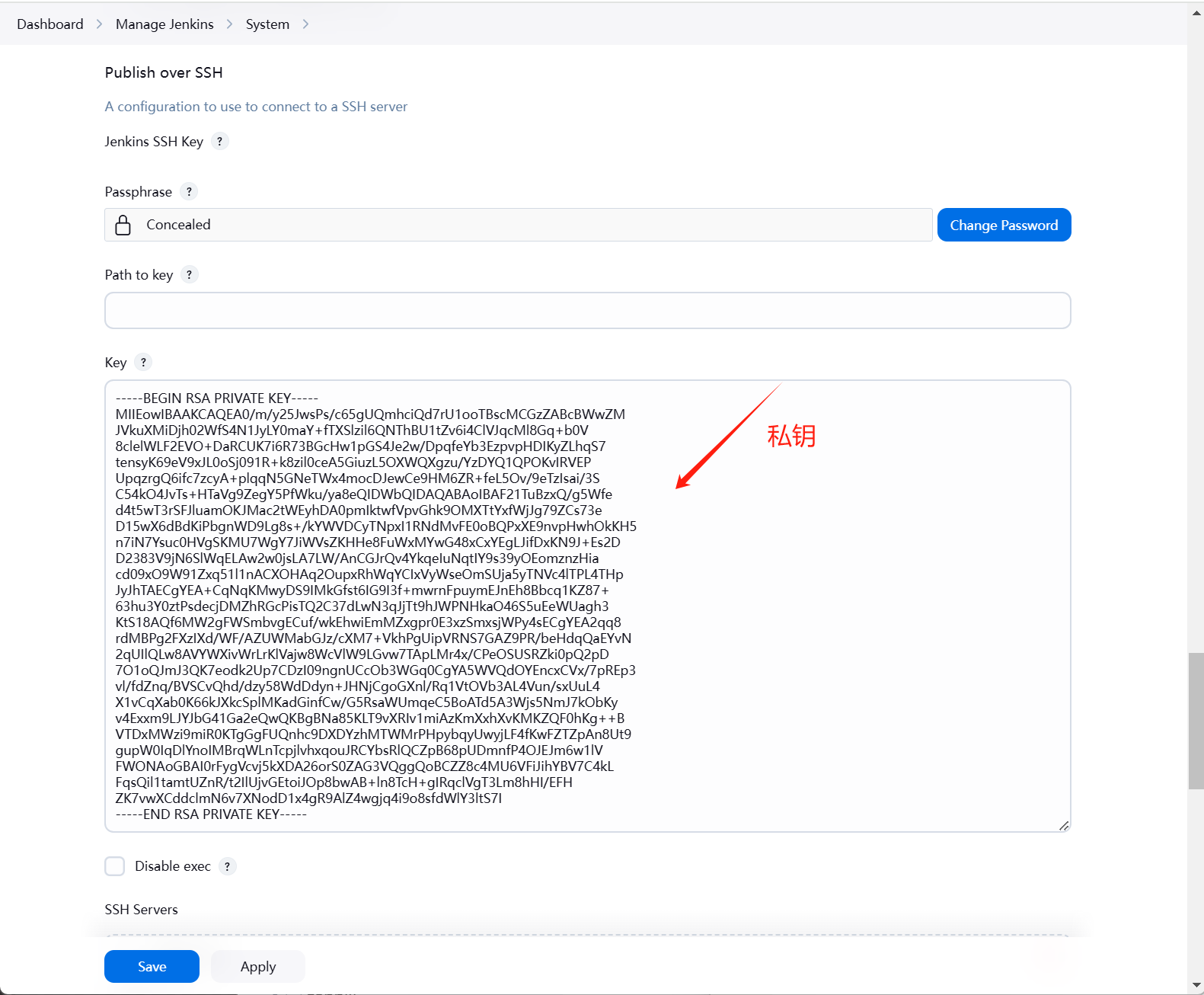
 jenins插件 一、汉化插件(不建议用 没什么用)Localization: Chinese二、凭证信息CloudBees Credentials Plugin三、docker插件Docker plugin四、k8s插件Kubernetes plugin五、连接推送到其他机器Publish Over SSH 六、基于角色管理权限(安装后需在全局安全配置-授权策略使用 Role-Based Strategy )Role-based Authorization Strategy 七、gitgit八、部署到 tomcatDeploy to container Plugin九、构建流水线风格PipeLine
jenins插件 一、汉化插件(不建议用 没什么用)Localization: Chinese二、凭证信息CloudBees Credentials Plugin三、docker插件Docker plugin四、k8s插件Kubernetes plugin五、连接推送到其他机器Publish Over SSH 六、基于角色管理权限(安装后需在全局安全配置-授权策略使用 Role-Based Strategy )Role-based Authorization Strategy 七、gitgit八、部署到 tomcatDeploy to container Plugin九、构建流水线风格PipeLine -
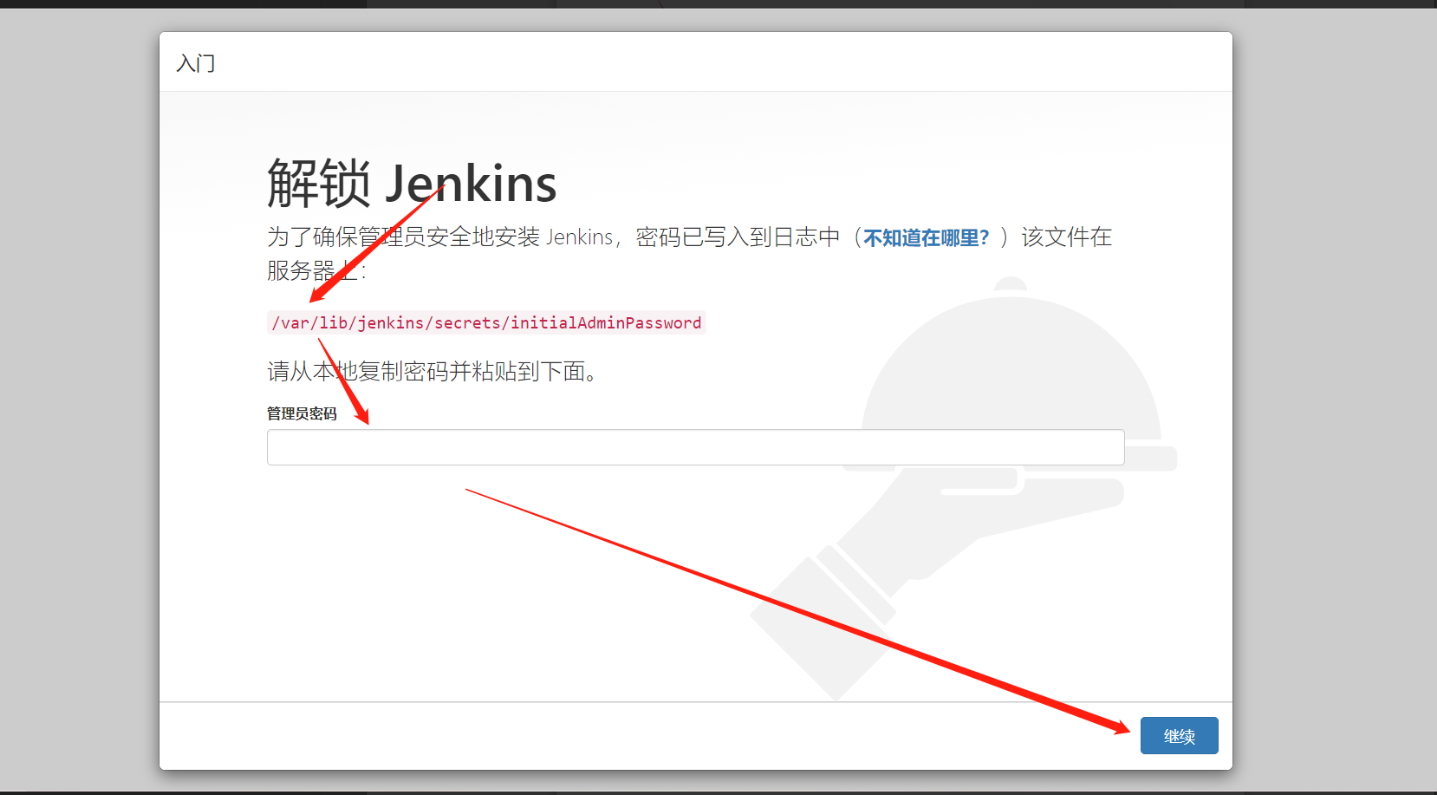
 Jenkins安装 新版的jenkins openjdk版本要17或者以上!!还有如果jenkins和gitlab一起安装在同一台机器上需要改gitlab的端口配置8080端口是会冲突!!一、Jenkins介绍Jenkins是一个自动化部署的工具。依赖于Java开发的,由各种组件组成的一个自动化部署工具。二、安装2.1 安装java环境yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk* -y2.2导入key (仅限yum安装)rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key2.3获取jenkins安装包wget https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/jenkins/redhat-stable/jenkins-2.249.1-1.1.noarch.rpm2.4安装jenkinsyum localinstall -y jenkins-2.249.1-1.1.noarch.rpm2.5启动jenkins并设置开机自启systemctl start jenkins systemctl enable jenkins三、页面访问并修改密码3.1输入自动生成的密码 /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword edfcd0f0432a4a868dc32da0c34f7f3a3.2自己选择插件安装3.3不安装插件,后面可以手动安装3.4设置用户名和密码然后登录四、优化4.1修改更新和搜索URLcd /var/lib/jenkins/updates sed -i 's/http:\/\/updates.jenkinsci.org\/download/https:\/\/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\/jenkins/g' default.json sed -i 's/http:\/\/www.google.com/https:\/\/www.baidu.com/g' default.json4.2修改站点升级为国内下载地址https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/jenkins/updates/update-center.json五、处理管理账号密码丢失问题vim /var/lib/jenkins/users/admin_7050982324762688703/config.xml <passwordHash>#jbcrypt:$2a$10$CEFbiUohDtWimNh4o3TBje2EEXgljqA/frbwED0Go5X533dd.jk6W</passwordHash> 替换成 <passwordHash>#jbcrypt:$2a$10$MiIVR0rr/UhQBqT.bBq0QehTiQVqgNpUGyWW2nJObaVAM/2xSQdSq</passwordHash> 然后密码使用123456登录
Jenkins安装 新版的jenkins openjdk版本要17或者以上!!还有如果jenkins和gitlab一起安装在同一台机器上需要改gitlab的端口配置8080端口是会冲突!!一、Jenkins介绍Jenkins是一个自动化部署的工具。依赖于Java开发的,由各种组件组成的一个自动化部署工具。二、安装2.1 安装java环境yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk* -y2.2导入key (仅限yum安装)rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key2.3获取jenkins安装包wget https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/jenkins/redhat-stable/jenkins-2.249.1-1.1.noarch.rpm2.4安装jenkinsyum localinstall -y jenkins-2.249.1-1.1.noarch.rpm2.5启动jenkins并设置开机自启systemctl start jenkins systemctl enable jenkins三、页面访问并修改密码3.1输入自动生成的密码 /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword edfcd0f0432a4a868dc32da0c34f7f3a3.2自己选择插件安装3.3不安装插件,后面可以手动安装3.4设置用户名和密码然后登录四、优化4.1修改更新和搜索URLcd /var/lib/jenkins/updates sed -i 's/http:\/\/updates.jenkinsci.org\/download/https:\/\/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\/jenkins/g' default.json sed -i 's/http:\/\/www.google.com/https:\/\/www.baidu.com/g' default.json4.2修改站点升级为国内下载地址https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/jenkins/updates/update-center.json五、处理管理账号密码丢失问题vim /var/lib/jenkins/users/admin_7050982324762688703/config.xml <passwordHash>#jbcrypt:$2a$10$CEFbiUohDtWimNh4o3TBje2EEXgljqA/frbwED0Go5X533dd.jk6W</passwordHash> 替换成 <passwordHash>#jbcrypt:$2a$10$MiIVR0rr/UhQBqT.bBq0QehTiQVqgNpUGyWW2nJObaVAM/2xSQdSq</passwordHash> 然后密码使用123456登录